The LRRC8-mediated volume-regulated anion channel is altered in glaucoma
- PMID: 30931966
- PMCID: PMC6443673
- DOI: 10.1038/s41598-019-41524-3
The LRRC8-mediated volume-regulated anion channel is altered in glaucoma
Erratum in
-
Author Correction: The LRRC8-mediated volume-regulated anion channel is altered in glaucoma.Sci Rep. 2020 Jul 7;10(1):11443. doi: 10.1038/s41598-020-68525-x. Sci Rep. 2020. PMID: 32632252 Free PMC article.
Abstract
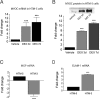
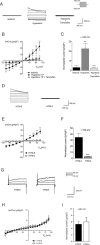
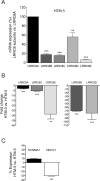
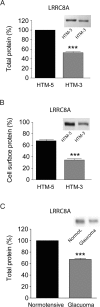
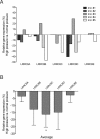
Regulation of cellular volume is an essential process to balance volume changes during cell proliferation and migration or when intracellular osmolality increases due to transepithelial transport. We previously characterized the key role of volume-regulated anion channels (VRAC) in the modulation of the volume of trabecular meshwork (TM) cells and, in turn, the aqueous humour (AH) outflow from the eye. The balance between the secretion and the drainage of AH determines the intraocular pressure (IOP) that is the major casual risk factor for glaucoma. Glaucoma is an ocular disease that causes irreversible blindness due to the degeneration of retinal ganglion cells. The recent identification of Leucine-Rich Repeat-Containing 8 (LRRC8A-E) proteins as the molecular components of VRAC opens the field to elucidate their function in the physiology of TM and glaucoma. Human TM cells derived from non-glaucomatous donors and from open-angle glaucoma patients were used to determine the expression and the functional activity of LRRC8-mediated channels. Expression levels of LRRC8A-E subunits were decreased in HTM glaucomatous cells compared to normotensive HTM cells. Consequently, the activity of VRAC currents and volume regulation of TM cells were significantly affected. Impaired cell volume regulation will likely contribute to altered aqueous outflow and intraocular pressure.
Conflict of interest statement
The authors declare no competing interests.
Figures


References
-
- Gual A, et al. Effects of time of storage, albumin, and osmolality changes on outflow facility (C) of bovine anterior segment in vitro. Investig. Ophthalmol. Vis. Sci. 1997;38:2165–2171. - PubMed

