Metabolic disturbances in synovial fluid are involved in the onset of synovitis in heifers with acute ruminal acidosis
- PMID: 30932023
- PMCID: PMC6443794
- DOI: 10.1038/s41598-019-42007-1
Metabolic disturbances in synovial fluid are involved in the onset of synovitis in heifers with acute ruminal acidosis
Abstract
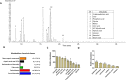
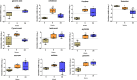
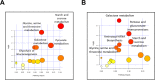
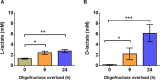
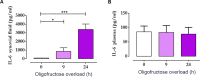
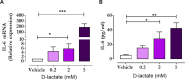
Acute ruminal acidosis (ARA) is the result of increased intake of highly fermentable carbohydrates, which frequently occurs in dairy cattle and is associated with aseptic polysynovitis. To characterise the metabolic changes in the joints of animals with ARA, we performed an untargeted gas chromatography-mass spectrometry (GC-MS)-based metabolomic analysis of synovial fluid. Seven heifers were challenged with an intraruminal oligofructose overload (13 g/kg of body weight [BW]) dissolved in water. Synovial fluid samples were collected at 0, 9 and 24 h post-overload. Metabolome analysis revealed the presence of 67 metabolites. At 9 h post-overload, glyceric acid, cellobiose, fructose and lactic acid were all increased, whereas at 24 h, sorbitol, lactic acid and fructose levels were all increased >10-fold. At 24 h, citric acid and threonine levels were significantly reduced. We detected increased L- and D-lactate, and the presence of interleukin-6 (IL-6) in synovial fluid. Furthermore, using bovine fibroblast-like synoviocytes, we observed that D-lactate induces IL-6 synthesis. Our results suggest that ARA produces severe metabolomic changes in synovial fluid, including disturbances in starch and sucrose metabolism, and increased lactate levels. These changes were observed prior to the appearance of synovitis, suggesting a potential role in the onset of polysynovitis.
Conflict of interest statement
The authors declare no competing interests.
Figures



Similar articles
-
The D-lactate enigma: exploring the inflammatory influence of D-lactate in cattle.Front Vet Sci. 2024 Dec 18;11:1509399. doi: 10.3389/fvets.2024.1509399. eCollection 2024. Front Vet Sci. 2024. PMID: 39744722 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Pro-inflammatory mediators and neutrophils are increased in synovial fluid from heifers with acute ruminal acidosis.BMC Vet Res. 2019 Jul 3;15(1):225. doi: 10.1186/s12917-019-1974-x. BMC Vet Res. 2019. PMID: 31269952 Free PMC article.
-
Polysynovitis after oligofructose overload in dairy cattle.J Comp Pathol. 2010 Feb-Apr;142(2-3):129-38. doi: 10.1016/j.jcpa.2009.09.001. Epub 2009 Dec 24. J Comp Pathol. 2010. PMID: 20034634
-
Metabolic Reprogramming and Inflammatory Response Induced by D-Lactate in Bovine Fibroblast-Like Synoviocytes Depends on HIF-1 Activity.Front Vet Sci. 2021 Mar 16;8:625347. doi: 10.3389/fvets.2021.625347. eCollection 2021. Front Vet Sci. 2021. PMID: 33796579 Free PMC article.
-
Ruminal acidosis in beef cattle: the current microbiological and nutritional outlook.J Dairy Sci. 2007 Jun;90 Suppl 1:E17-38. doi: 10.3168/jds.2006-478. J Dairy Sci. 2007. PMID: 17517750 Review.
Cited by
-
The D-lactate enigma: exploring the inflammatory influence of D-lactate in cattle.Front Vet Sci. 2024 Dec 18;11:1509399. doi: 10.3389/fvets.2024.1509399. eCollection 2024. Front Vet Sci. 2024. PMID: 39744722 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Lactic Acidosis Related to Pharmacotherapy and Human Diseases.Pharmaceuticals (Basel). 2022 Nov 30;15(12):1496. doi: 10.3390/ph15121496. Pharmaceuticals (Basel). 2022. PMID: 36558947 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Andrographolide Ameliorates Inflammatory Changes Induced by D-Lactate in Bovine Fibroblast-like Synoviocytes.Animals (Basel). 2024 Mar 19;14(6):936. doi: 10.3390/ani14060936. Animals (Basel). 2024. PMID: 38540033 Free PMC article.
-
Synergistic Responses of Tibetan Sheep Rumen Microbiota, Metabolites, and the Host to the Plateau Environment.Int J Mol Sci. 2023 Oct 3;24(19):14856. doi: 10.3390/ijms241914856. Int J Mol Sci. 2023. PMID: 37834304 Free PMC article.
-
Alterations in Rumen Bacterial Community and Metabolome Characteristics of Cashmere Goats in Response to Dietary Nutrient Density.Animals (Basel). 2020 Jul 14;10(7):1193. doi: 10.3390/ani10071193. Animals (Basel). 2020. PMID: 32674381 Free PMC article.
References
-
- Castillo-González A, Burrola-Barraza M, Domínguez-Viveros J, Chávez-Martínez A. Rumen microorganisms and fermentation. Arch. med. vet. 2014;46:349–361. doi: 10.4067/S0301-732X2014000300003. - DOI
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Miscellaneous

