Surgical Decision Making in Brain Hemorrhage
- PMID: 30932784
- PMCID: PMC6485298
- DOI: 10.1161/STROKEAHA.118.022694
Surgical Decision Making in Brain Hemorrhage
Abstract
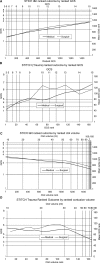
Background and Purpose- The STICH (Surgical Trial in Lobar Intracerebral Haemorrhage) I and II trials randomized patients with spontaneous intracerebral hemorrhage (ICH) to early surgery or initial conservative treatment. Both were nonsignificant; possibly because surgery has minimal effect on recovery, or because surgery benefits some and harms others. We introduce a new nonparametric method of analysis. The method is then applied to data from a third trial, STITCH(Trauma) (Surgical Trial in Traumatic Intracerebral Haemorrhage), which addressed a similar surgical question in head-injured patients. Methods- Data from 1541 patients from the STICH trials were analyzed using (1) standard meta-analysis of prognosis-based dichotomized outcome and prespecified standard subgroups of Glasgow Coma Scale (GCS): 3-8, 9-12, and 13-15; (2) new nonparametric regression of ranked Extended Glasgow Outcome Scale against ranked GCS and ranked volume; and (3) analysis (1) repeated using categories identified by analysis (2). Results- Standard meta-analysis showed more favorable outcomes, although nonsignificant, with surgery if presenting GCS was 9-12 (spontaneous ICH odds ratio, 0.70 [95% CI, 0.48-1.03; P=0.07]; traumatic odds ratio, 0.48 [95% CI, 0.18-1.26; P=0.14]). Ranked analysis showed a similar pattern of results for both spontaneous and traumatic ICH. Surgery was harmful for small lesions with increasing benefit for larger volumes. With GCS, surgery had little effect at either ends of the spectrum but suggested a beneficial effect in the range 10 to 13 (identified graphically). Repeating the meta-analysis with this categorization showed significant benefit for surgery (spontaneous odds ratio, 0.71 [95% CI, 0.51-1.00; P=0.05]; traumatic odds ratio, 0.16 [95% CI, 0.05-0.51; P=0.002]). Conclusions- The nonsignificant results observed in the STICH trials are because of mixing patients who benefit from surgery with those who are harmed. Patients with a GCS 10-13 or a large ICH are likely to benefit from surgery. Our analysis showed a similar effect on traumatic ICH/contusion data and promises to be a valuable tool. Clinical Trial Registration- URL: http://www.isrctn.com/ . Unique identifiers: ISRCTN19976990 (STITCH), ISRCTN22153967 (STICH II), and ISRCTN19321911 (STITCH[Trauma]).
Keywords: Glasgow Outcome Scale; cerebral hemorrhage; conservative treatment; decision making; surgery.
Figures


References
-
- Auer LM, Deinsberger W, Niederkorn K, Gell G, Kleinert R, Schneider G, et al. Endoscopic surgery versus medical treatment for spontaneous intracerebral hematoma: a randomized study. J Neurosurg. 1989;70:530–535. doi: 10.3171/jns.1989.70.4.0530. - PubMed
-
- Batjer HH, Reisch JS, Allen BC, Plaizier LJ, Su CJ. Failure of surgery to improve outcome in hypertensive putaminal hemorrhage. A prospective randomized trial. Arch Neurol. 1990;47:1103–1106. - PubMed
-
- Chen X, Wu J, Zhou X, YZhang Y, Wang Z, Qin Z, et al. The randomized multicentric prospective controlled trial in the standardized treatment of hypertensive intracerebral hematomas: the comparison of surgical therapeutic outcomes with conservative therapy. Chinese J Clin Neurosci. 2001;4:365–368.
-
- Chen X, Yang H, Cheng Z. A prospective randomised trial of surgical and conservative treatment for hypertensive intracerebral haemorrhage. Acta Acad Med Shanghai. 1992;19:237–240.
-
- Hattori N, Katayama Y, Maya Y, Gatherer A. Impact of stereotactic hematoma evacuation on activities of daily living during the chronic period following spontaneous putaminal hemorrhage: a randomized study. J Neurosurg. 2004;101:417–420. doi: 10.3171/jns.2004.101.3.0417. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Associated data
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Medical

