Epithelial cell-derived cytokines: more than just signaling the alarm
- PMID: 30932910
- PMCID: PMC6436879
- DOI: 10.1172/JCI124606
Epithelial cell-derived cytokines: more than just signaling the alarm
Abstract
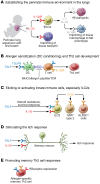
The epithelial cell-derived cytokines thymic stromal lymphopoietin (TSLP), IL-33, and IL-25 are central regulators of type 2 immunity, which drives a broad array of allergic responses. Often characterized as "alarmins" that are released by the barrier epithelium in response to external insults, these epithelial cell-derived cytokines were initially thought to act only early in allergic inflammation. Indeed, TSLP can condition dendritic cells to initiate type 2 responses, and IL-33 may influence susceptibility to asthma through its role in establishing the immune environment in the perinatal lungs. However, TSLP, IL-33, and IL-25 all regulate a broad spectrum of innate immune cell populations and are particularly potent in eliciting and activating type 2 innate lymphoid cells (ILC2s) that may act throughout allergic inflammation. Recent data suggest that a TSLP/ILC axis may mediate steroid resistance in asthma. Recent identification of memory Th2 cell subsets that are characterized by high receptor expression for TSLP, IL-33, and IL-25 further supports a role for these cytokines in allergic exacerbations. There is therefore growing interest in developing biologics that target TSLP, IL-33, and IL-25. This Review provides an overview of TSLP, IL-33, and IL-25 and the development of blocking antibodies that target these epithelial cell-derived cytokines.
Conflict of interest statement
Figures
References
-
- Rigas D, et al. Type 2 innate lymphoid cell suppression by regulatory T cells attenuates airway hyperreactivity and requires inducible T-cell costimulator-inducible T-cell costimulator ligand interaction. J Allergy Clin Immunol. 2017;139(5):1468–1477.e2. doi: 10.1016/j.jaci.2016.08.034. - DOI - PMC - PubMed
-
- Friend SL, Hosier S, Nelson A, Foxworthe D, Williams DE, Farr A. A thymic stromal cell line supports in vitro development of surface IgM+ B cells and produces a novel growth factor affecting B and T lineage cells. Exp Hematol. 1994;22(3):321–328. - PubMed

