Realizing the potential of magnetic resonance image guided radiotherapy in gynaecological and rectal cancer
- PMID: 30933550
- PMCID: PMC6592079
- DOI: 10.1259/bjr.20180670
Realizing the potential of magnetic resonance image guided radiotherapy in gynaecological and rectal cancer
Abstract
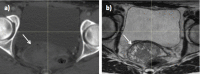
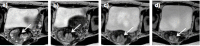
CT-based radiotherapy workflow is limited by poor soft tissue definition in the pelvis and reliance on rigid registration methods. Current image-guided radiotherapy and adaptive radiotherapy models therefore have limited ability to improve clinical outcomes. The advent of MRI-guided radiotherapy solutions provides the opportunity to overcome these limitations with the potential to deliver online real-time MRI-based plan adaptation on a daily basis, a true "plan of the day." This review describes the application of MRI guided radiotherapy in two pelvic tumour sites likely to benefit from this approach.
Figures



References
-
- Laursen LV , Elstrøm UV , Vestergaard A , Muren LP , Petersen JB , Lindegaard JC , et al. . Residual rotational set-up errors after daily cone-beam CT image guided radiotherapy of locally advanced cervical cancer . Radiother Oncol 2012. ; 105 : 220 – 5 . doi: 10.1016/j.radonc.2012.08.012 - DOI - PubMed
-
- Roeske JC , Lujan A , Rotmensch J , Waggoner SE , Yamada D , Mundt AJ . Intensity-modulated whole pelvic radiation therapy in patients with gynecologic Malignancies . International Journal of Radiation Oncology*Biology*Physics 2000. ; 48 : 1613 – 21 . doi: 10.1016/S0360-3016(00)00771-9 - DOI - PubMed
-
- Duthoy W , De Gersem W , Vergote K , Boterberg T , Derie C , Smeets P , et al. . Clinical implementation of intensity-modulated Arc therapy (IMAT) for rectal cancer . International Journal of Radiation Oncology*Biology*Physics 2004. ; 60 : 794 – 806 . doi: 10.1016/j.ijrobp.2004.04.016 - DOI - PubMed
-
- van Herk M , Remeijer P , Rasch C , Lebesque JV . The probability of correct target dosage: dose-population histograms for deriving treatment margins in radiotherapy . International Journal of Radiation Oncology*Biology*Physics 2000. ; 47 : 1121 – 35 . doi: 10.1016/S0360-3016(00)00518-6 - DOI - PubMed

