Molecular pathogenic pathways in extranodal NK/T cell lymphoma
- PMID: 30935402
- PMCID: PMC6444858
- DOI: 10.1186/s13045-019-0716-7
Molecular pathogenic pathways in extranodal NK/T cell lymphoma
Abstract
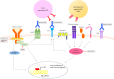
Extranodal NK/T cell lymphoma, nasal type (ENKTL) is an aggressive malignancy with a dismal prognosis. Although L-asparaginase-based chemotherapy has resulted in improved response rates, relapse occurs in up to 50% of patients with disseminated disease. There is hence an urgent need for effective targeted therapy, especially for patients with relapsed or refractory disease. Novel insights gleaned from high-throughput molecular and genomic profiling studies in recent years have contributed significantly to the understanding of the molecular biology of ENKTL, which exemplifies many of the hallmarks of cancer. Deregulated pro-proliferative signaling pathways, such as the Janus-associated kinase/signal transducer and activator of transcription (JAK/STAT), platelet-derived growth factor (PDGF), Aurora kinase, MYC, and NF-κB, have been identified as potential therapeutic targets. The discovery of the non-canonical function of EZH2 as a pro-proliferative transcriptional co-activator has shed further light on the pathogenesis of ENKTL. Loss of key tumor suppressor genes located on chromosome 6q21 also plays an important role. The best-studied examples include PR domain zinc finger protein 1(PRDM1), protein tyrosine phosphatase kappa (PTPRK), and FOXO3. Promoter hypermethylation has been shown to result in the downregulation of other tumor suppressor genes in ENKTL, which may be potentially targeted through hypomethylating agents. Deregulation of apoptosis through p53 mutations and upregulation of the anti-apoptotic protein, survivin, may provide a further growth advantage to this tumor. A deranged DNA damage response as a result of the aberration of ataxia telangiectasia-related (ATR) kinases can lead to significant genomic instability and may contribute to chemoresistance of ENKTL. Recently, immune evasion has emerged as a critical pathway for survival in ENKTL and may be a consequence of HLA dysregulation or STAT3-driven upregulation of programmed cell death ligand 1 (PD-L1). Immunotherapy via inhibition of programmed cell death 1 (PD-1)/PD-L1 checkpoint signaling holds great promise as a novel therapeutic option. In this review, we present an overview of the key molecular and pathogenic pathways in ENKTL, organized using the framework of the "hallmarks of cancer" as described by Hanahan and Weinberg, with a focus on those with the greatest translational potential.
Keywords: Extranodal NK/T cell lymphoma; Hallmarks of cancer; Molecular pathogenesis.
Conflict of interest statement
Authors’ information
Not applicable
Ethics approval and consent to participate
Not applicable
Consent for publication
Not applicable
Competing interests
The authors declare that they have no competing interests.
Publisher’s Note
Springer Nature remains neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations.
Figures

References
-
- Chan JKC, Quintanilla-Martinez L, Ferry JA, et al. Extranodal NK/T-cell lymphoma, nasal type. In: Swerdlow SH, Campo E, Harris NL, Jaffe ES, Pileri SA, Stein H, et al., editors. WHO classification of tumours of haematopoietic and lymphoid tissues. Lyon: International Agency for Research on Cancer; 2017. pp. 368–371.
-
- Lemonnier F, Gaulard P, de Leval L. New insights in the pathogenesis of T-cell lymphomas. Curr Opin Oncol. 2018;30(5):277–284. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Research Materials
Miscellaneous

