Efficacy and safety assessment of a TRAF6-targeted nanoimmunotherapy in atherosclerotic mice and non-human primates
- PMID: 30936448
- PMCID: PMC6447057
- DOI: 10.1038/s41551-018-0221-2
Efficacy and safety assessment of a TRAF6-targeted nanoimmunotherapy in atherosclerotic mice and non-human primates
Erratum in
-
Author Correction: Efficacy and safety assessment of a TRAF6-targeted nanoimmunotherapy in atherosclerotic mice and non-human primates.Nat Biomed Eng. 2018 Aug;2(8):623. doi: 10.1038/s41551-018-0281-3. Nat Biomed Eng. 2018. PMID: 31015637
Abstract
Macrophage accumulation in atherosclerosis is directly linked to the destabilization and rupture of plaque, causing acute atherothrombotic events. Circulating monocytes enter the plaque and differentiate into macrophages, where they are activated by CD4+ T lymphocytes through CD40-CD40 ligand signalling. Here, we report the development and multiparametric evaluation of a nanoimmunotherapy that moderates CD40-CD40 ligand signalling in monocytes and macrophages by blocking the interaction between CD40 and tumour necrosis factor receptor-associated factor 6 (TRAF6). We evaluated the biodistribution characteristics of the nanoimmunotherapy in apolipoprotein E-deficient (Apoe-/-) mice and in non-human primates by in vivo positron-emission tomography imaging. In Apoe-/- mice, a 1-week nanoimmunotherapy treatment regimen achieved significant anti-inflammatory effects, which was due to the impaired migration capacity of monocytes, as established by a transcriptome analysis. The rapid reduction of plaque inflammation by the TRAF6-targeted nanoimmunotherapy and its favourable toxicity profiles in both mice and non-human primates highlights the translational potential of this strategy for the treatment of atherosclerosis.
Figures

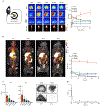
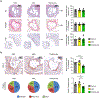
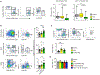
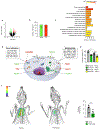

Comment in
-
Nanoimmunotherapy targeting CD40-TRAF6 signalling to reduce atherosclerosis.Nat Rev Cardiol. 2018 Jun;15(6):317. doi: 10.1038/s41569-018-0024-x. Nat Rev Cardiol. 2018. PMID: 29717214 No abstract available.
References
-
- Schönbeck U, Libby P CD40 signaling and plaque instability. Circ. Res. 89, 1092–103 (2001). - PubMed
-
- Lutgens E et al. Requirement for CD154 in the progression of atherosclerosis. Nat. Med. 5, 1313–6 (1999). - PubMed
-
- Mach F, Schönbeck U, Sukhova GK, Atkinson E, Libby P Reduction of atherosclerosis in mice by inhibition of CD40 signalling. Nature. 394, 200–3 (1998). - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Medical
Research Materials
Miscellaneous

