Platelet GPIbα is a mediator and potential interventional target for NASH and subsequent liver cancer
- PMID: 30936549
- PMCID: PMC12452109
- DOI: 10.1038/s41591-019-0379-5
Platelet GPIbα is a mediator and potential interventional target for NASH and subsequent liver cancer
Erratum in
-
Author Correction: Platelet GPIbα is a mediator and potential interventional target for NASH and subsequent liver cancer.Nat Med. 2022 Mar;28(3):600. doi: 10.1038/s41591-022-01693-7. Nat Med. 2022. PMID: 35181768 No abstract available.
Abstract
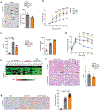
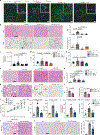
Non-alcoholic fatty liver disease ranges from steatosis to non-alcoholic steatohepatitis (NASH), potentially progressing to cirrhosis and hepatocellular carcinoma (HCC). Here, we show that platelet number, platelet activation and platelet aggregation are increased in NASH but not in steatosis or insulin resistance. Antiplatelet therapy (APT; aspirin/clopidogrel, ticagrelor) but not nonsteroidal anti-inflammatory drug (NSAID) treatment with sulindac prevented NASH and subsequent HCC development. Intravital microscopy showed that liver colonization by platelets depended primarily on Kupffer cells at early and late stages of NASH, involving hyaluronan-CD44 binding. APT reduced intrahepatic platelet accumulation and the frequency of platelet-immune cell interaction, thereby limiting hepatic immune cell trafficking. Consequently, intrahepatic cytokine and chemokine release, macrovesicular steatosis and liver damage were attenuated. Platelet cargo, platelet adhesion and platelet activation but not platelet aggregation were identified as pivotal for NASH and subsequent hepatocarcinogenesis. In particular, platelet-derived GPIbα proved critical for development of NASH and subsequent HCC, independent of its reported cognate ligands vWF, P-selectin or Mac-1, offering a potential target against NASH.
Conflict of interest statement
Competing interests
J.M.L. receives consulting fees from Bayer HealthCare Pharmaceuticals, Eli Lilly, Bristol-Myers Squibb, Merck, Eisai Inc, Celsion Corporation, Exelixis, Merck, Ipsen, Glycotest, Navigant, Leerink Swann LLC, Midatech Ltd, Fortress Biotech, Sprink Pharmaceuticals and Nucleix and research support from Bayer HealthCare Pharmaceuticals, Eisai Inc, Bristol-Myers Squibb and Ipsen. This article presents independent research supported in part by the National Institute for Health Research (NIHR) Birmingham Biomedical Research Centre. The views expressed are those of the author(s) and not necessarily those of the National Health Service, the NIHR, or the Department of Health.
Figures














Comment in
-
Platelets with dangerous cargo.Nat Rev Cancer. 2019 Jun;19(6):302. doi: 10.1038/s41568-019-0146-4. Nat Rev Cancer. 2019. PMID: 31036885 No abstract available.
-
The effects of platelet accumulation in fatty liver disease.Nat Rev Gastroenterol Hepatol. 2019 Jul;16(7):393-394. doi: 10.1038/s41575-019-0160-8. Nat Rev Gastroenterol Hepatol. 2019. PMID: 31114057 No abstract available.
-
Small but Mighty: Platelets in NASH and Other Chronic Liver Diseases.Hepatology. 2020 Apr;71(4):1501-1504. doi: 10.1002/hep.31101. Epub 2020 Mar 18. Hepatology. 2020. PMID: 31903616 Free PMC article. No abstract available.
References
-
- Fleet SE, Lefhowitch JH & Lavine JE Current concepts in pediatric nonalcoholic fatty liver disease. Gastroenterol. Clin. North Am 46, 217–231 (2017). - PubMed
-
- European Association for the Study of the Liver, European Association for the Study of Diabetes & European Association for the Study of Obesity. EASL-EASD-EASO Clinical Practice Guidelines for the management of non-alcoholic fatty liver disease. J. Hepatol 64, 1388–1402 (2016). - PubMed
-
- Younossi Z et al. Global perspectives on non-alcoholic fatty liver disease and non-alcoholic steatohepatitis. Hepatology 10.1002/hep.30251 (2018). - DOI
-
- Brunt EM et al. Nonalcoholic fatty liver disease. Nat. Rev. Dis. Primers 1, 15080 (2015). - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
- G0300101/MRC_/Medical Research Council/United Kingdom
- G0300102/MRC_/Medical Research Council/United Kingdom
- G0700301/MRC_/Medical Research Council/United Kingdom
- MR/K001949/1/MRC_/Medical Research Council/United Kingdom
- WT_/Wellcome Trust/United Kingdom
- MC_PC_14123/MRC_/Medical Research Council/United Kingdom
- G0400496/MRC_/Medical Research Council/United Kingdom
- 23390/CRUK_/Cancer Research UK/United Kingdom
- MR/M009157/1/MRC_/Medical Research Council/United Kingdom
- 26813/CRUK_/Cancer Research UK/United Kingdom
- G0802577/MRC_/Medical Research Council/United Kingdom
- P30 CA196521/CA/NCI NIH HHS/United States
- MC_U120097114/MRC_/Medical Research Council/United Kingdom
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Medical
Molecular Biology Databases
Research Materials
Miscellaneous

