Inferring population dynamics from single-cell RNA-sequencing time series data
- PMID: 30936567
- PMCID: PMC7397487
- DOI: 10.1038/s41587-019-0088-0
Inferring population dynamics from single-cell RNA-sequencing time series data
Abstract
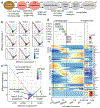
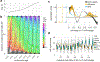
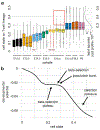
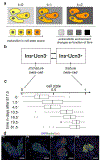
Recent single-cell RNA-sequencing studies have suggested that cells follow continuous transcriptomic trajectories in an asynchronous fashion during development. However, observations of cell flux along trajectories are confounded with population size effects in snapshot experiments and are therefore hard to interpret. In particular, changes in proliferation and death rates can be mistaken for cell flux. Here we present pseudodynamics, a mathematical framework that reconciles population dynamics with the concepts underlying developmental trajectories inferred from time-series single-cell data. Pseudodynamics models population distribution shifts across trajectories to quantify selection pressure, population expansion, and developmental potentials. Applying this model to time-resolved single-cell RNA-sequencing of T-cell and pancreatic beta cell maturation, we characterize proliferation and apoptosis rates and identify key developmental checkpoints, data inaccessible to existing approaches.
Conflict of interest statement
CONFLICT OF INTEREST
The authors declare no competing interests.
Figures

References
Main references
-
- Taniguchi K, Kajiyama T & Kambara H. Quantitative analysis of gene expression in a single cell by qPCR. Nat. Methods 6, 503–506 (2009). - PubMed
-
- Bandura DR et al. Mass cytometry: technique for real time single cell multitarget immunoassay based on inductively coupled plasma time-of-flight mass spectrometry. Anal. Chem. 81, 6813–6822 (2009). - PubMed
-
- Haghverdi L, Büttner M, Wolf FA, Buettner F & Theis FJ Diffusion pseudotime robustly reconstructs lineage branching. Nat. Methods 13, 845–848 (2016). - PubMed
Methods references
-
- Cohen SD, Hindmarsh AC & Dubois PF CVODE, a stiff/nonstiff ODE solver in C. Computers in physics (1996).
-
- Fröhlich F, Theis FJ, Rädler JO & Hasenauer J. Parameter estimation for dynamical systems with discrete events and logical operations. Bioinformatics 33, 1049–1056 (2017). - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Molecular Biology Databases

