Integrating herbarium specimen observations into global phenology data systems
- PMID: 30937223
- PMCID: PMC6426164
- DOI: 10.1002/aps3.1231
Integrating herbarium specimen observations into global phenology data systems
Abstract
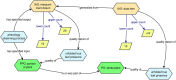
Premise of the study: The Plant Phenology Ontology (PPO) was originally developed to integrate phenology observations of whole plants across different global observation networks. Here we describe a new release of the PPO and associated data pipelines that supports integration of phenology observations from herbarium specimens, which provide historical and modern phenology data.
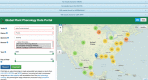
Methods and results: Critical changes to the PPO include key terms that describe how measurements from parts of plants, which are captured in most imaged herbarium specimens, relate to whole plants. We provide proof of concept for ingesting annotations from imaged herbarium sheets of Prunus serotina, the common black cherry. We then provide an example analysis of changes in flowering timing over the past 125 years, demonstrating the value of integrating herbarium and observational phenology data sets.
Conclusions: These conceptual and technical advances will support the addition of phenology data from herbaria, but also could be expanded upon to facilitate the inclusion of data from photograph-based citizen science platforms. With the incorporation of herbarium phenology data, new historical baseline data will strengthen the capability to monitor, model, and forecast plant phenology changes.
Keywords: data integration; herbarium specimens; knowledge representation; ontology; plant phenology.
Figures

References
-
- Bertin, R. I. 2008. Plant phenology and distribution in relation to recent climate change. Journal of the Torrey Botanical Society 135: 126–146.
-
- Ceusters, W. 2012. An information artifact ontology perspective on data collections and associated representational artifacts. Studies in Health Technology and Informatics 180: 68–72. - PubMed
-
- Chmielewski, F.‐M. , Müller A., and Bruns E.. 2004. Climate changes and trends in phenology of fruit trees and field crops in Germany, 1961–2000. Agricultural and Forest Meteorology 121: 69–78.
-
- Chuine, I. , and Régnière J.. 2017. Process‐based models of phenology for plants and animals. Annual Review of Ecology, Evolution, and Systematics 48: 159–182.
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Research Materials
Miscellaneous

