Calculation of a Primary Immunodeficiency "Risk Vital Sign" via Population-Wide Analysis of Claims Data to Aid in Clinical Decision Support
- PMID: 30937298
- PMCID: PMC6431644
- DOI: 10.3389/fped.2019.00070
Calculation of a Primary Immunodeficiency "Risk Vital Sign" via Population-Wide Analysis of Claims Data to Aid in Clinical Decision Support
Abstract
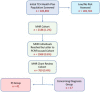
Background: Early diagnosis of primary immunodeficiency disease leads to reductions in illness and decreased healthcare costs. Analysis of electronic health record data may allow for identification of persons at risk of host-defense impairments from within the general population. Our hypothesis was that coded infection history would inform individual risk of disease and ultimately lead to diagnosis. Methods: In this study we assessed individual risk for primary immunodeficiency by analyzing diagnostic codes and pharmacy records from members (n = 185,892) of a large pediatric health network. Relevant infection-associated diagnostic codes were weighted and enumerated for individual members allowing for risk score calculations ("Risk Vital Sign"). At-risk individuals underwent further assessment by chart review and re-analysis of diagnostic codes 12 months later. Results: Of the original cohort, 2188 (1.2%) individuals were identified as medium-high-risk for having a primary immunodeficiency. This group included 41 subjects who were ultimately diagnosed with primary immunodeficiency. An additional 57 medium-high risk patients had coded diagnoses worthy of referral. Conclusions: Population-wide informatics approaches can facilitate disease detection and improve outcomes. Early identification of the 98 patients with confirmed or suspected primary immunodeficiency described here could represent an annual cost savings of up to $7.7 million US Dollars.
Keywords: big data and analytics; biomedical informatics; biomedical informatics and mathematics; primary immumunodeficiencies; public health.
Figures

References
-
- NIH Strategic Plan for Data Science NIH Strategic Plan for Data Science. (2017). Available online at: https://grants.nih.gov/grants/rfi/NIH-Strategic-Plan-for-Data-Science.pdf
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources

