Towards a solution to MERS: protective human monoclonal antibodies targeting different domains and functions of the MERS-coronavirus spike glycoprotein
- PMID: 30938227
- PMCID: PMC6455120
- DOI: 10.1080/22221751.2019.1597644
Towards a solution to MERS: protective human monoclonal antibodies targeting different domains and functions of the MERS-coronavirus spike glycoprotein
Abstract
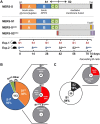
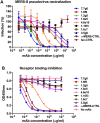
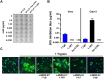
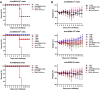
The Middle-East respiratory syndrome coronavirus (MERS-CoV) is a zoonotic virus that causes severe and often fatal respiratory disease in humans. Efforts to develop antibody-based therapies have focused on neutralizing antibodies that target the receptor binding domain of the viral spike protein thereby blocking receptor binding. Here, we developed a set of human monoclonal antibodies that target functionally distinct domains of the MERS-CoV spike protein. These antibodies belong to six distinct epitope groups and interfere with the three critical entry functions of the MERS-CoV spike protein: sialic acid binding, receptor binding and membrane fusion. Passive immunization with potently as well as with poorly neutralizing antibodies protected mice from lethal MERS-CoV challenge. Collectively, these antibodies offer new ways to gain humoral protection in humans against the emerging MERS-CoV by targeting different spike protein epitopes and functions.
Keywords: Coronavirus; MERS; antibodies; spike protein.
Figures

References
-
- Haagmans B. L., Al Dhahiry S. H., Reusken C. B., Raj V. S., Galiano M., Myers R., Godeke G. J., Jonges M., Farag E., Diab A., Ghobashy H., Alhajri F., Al-Thani M., Al-Marri S. A., Al Romaihi H. E., Al Khal A., Bermingham A., Osterhaus A. D., AlHajri M. M., and Koopmans M. P.. 2014. Middle East respiratory syndrome coronavirus in dromedary camels: an outbreak investigation. Lancet Infect. Dis. 14:140–145. doi:10.1016/S1473-3099(13)70690-X. - DOI - PMC - PubMed
-
- Memish Z. A., Cotten M., Meyer B., Watson S. J., Alsahafi A. J., Al Rabeeah A. A., Corman V. M., Sieberg A., Makhdoom H. Q., Assiri A., Al Masri M., Aldabbagh S., Bosch B. J., Beer M., Muller M. A., Kellam P., and Drosten C.. 2014. Human infection with MERS coronavirus after exposure to infected camels, Saudi Arabia, 2013. Emerg Infect Dis 20:1012–1015. doi:10.3201/eid2006.140402. - DOI - PMC - PubMed
