Phase II Study of Lenvatinib in Patients With Progressive, Recurrent or Metastatic Adenoid Cystic Carcinoma
- PMID: 30939095
- PMCID: PMC6599407
- DOI: 10.1200/JCO.18.01859
Phase II Study of Lenvatinib in Patients With Progressive, Recurrent or Metastatic Adenoid Cystic Carcinoma
Abstract
Purpose: Recurrent or metastatic adenoid cystic carcinoma (R/M ACC) is a malignant neoplasm of predominantly salivary gland origin for which effective therapies are lacking. We conducted a phase II trial evaluating the multitargeted tyrosine kinase inhibitor lenvatinib in patients with R/M ACC.
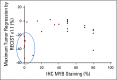
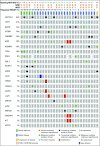
Patients and methods: This study was conducted with a two-stage minimax design. Patients with histologically confirmed R/M ACC of any primary site with radiographic and/or symptomatic progression were eligible. Any prior therapy was allowed except previous lenvatinib. Patients received lenvatinib 24 mg orally per day. The primary end point was overall response rate. Secondary end points were progression-free survival and safety. An exploratory analysis of how MYB expression and genomic alterations relate to outcomes was conducted.
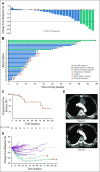
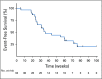
Results: Thirty-three patients were enrolled; 32 were evaluable for the primary end point. Five patients (15.6%) had a confirmed partial response, 24 patients (75%) had stable disease, two patients (6.3%) discontinued treatment as a result of toxicity before the first scan, and one patient (3.1%) had progression of disease as best response. Median progression-free survival time was 17.5 months (95% CI, 7.2 months to not reached), although only eight progression events were observed. Patients otherwise were removed for toxicity (n = 5), as a result of withdrawal of consent (n = 9), or at the treating physician's discretion (n = 6). Twenty-three patients required at least one dose modification, and 18 of 32 patients discontinued lenvatinib for drug-related issues. The most common grade 3 or 4 adverse events were hypertension (n = 9; 28.1%) and oral pain (n = 3; 9.4%). Three grade 4 adverse events were observed (myocardial infarction, n = 1; posterior reversible encephalopathy syndrome, n = 1; and intracranial hemorrhage, n = 1).
Conclusion: This trial met the prespecified overall response rate primary end point, demonstrating antitumor activity with lenvatinib in R/M ACC patients. Toxicity was comparable to previous studies, requiring monitoring and management.
Figures
References
-
- Spiro RH. Distant metastasis in adenoid cystic carcinoma of salivary origin. Am J Surg. 1997;174:495–498. - PubMed
-
- Chau NG, Hotte SJ, Chen EX, et al. A phase II study of sunitinib in recurrent and/or metastatic adenoid cystic carcinoma (ACC) of the salivary glands: Current progress and challenges in evaluating molecularly targeted agents in ACC. Ann Oncol. 2012;23:1562–1570. - PubMed
-
- Thomson DJ, Silva P, Denton K, et al. Phase II trial of sorafenib in advanced salivary adenoid cystic carcinoma of the head and neck. Head Neck. 2015;37:182–187. - PubMed
-
- Locati LD, Perrone F, Cortelazzi B, et al. A phase II study of sorafenib in recurrent and/or metastatic salivary gland carcinomas: Translational analyses and clinical impact. Eur J Cancer. 2016;69:158–165. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Miscellaneous

