Magnetic Strategies for Nervous System Control
- PMID: 30939100
- PMCID: PMC6617523
- DOI: 10.1146/annurev-neuro-070918-050241
Magnetic Strategies for Nervous System Control
Abstract
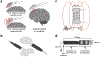
Magnetic fields pass through tissue undiminished and without producing harmful effects, motivating their use as a wireless, minimally invasive means to control neural activity. Here, we review mechanisms and techniques coupling magnetic fields to changes in electrochemical potentials across neuronal membranes. Biological magnetoreception, although incompletely understood, is discussed as a potential source of inspiration. The emergence of magnetic properties in materials is reviewed to clarify the distinction between biomolecules containing transition metals and ferrite nanoparticles that exhibit significant net moments. We describe recent developments in the use of magnetic nanomaterials as transducers converting magnetic stimuli to forms readily perceived by neurons and discuss opportunities for multiplexed and bidirectional control as well as the challenges posed by delivery to the brain. The variety of magnetic field conditions and mechanisms by which they can be coupled to neuronal signaling cascades highlights the desirability of continued interchange between magnetism physics and neurobiology.
Keywords: magnetic field; magnetic nanoparticles; magnetic stimulation; magnetoreception; neuromodulation.
Figures



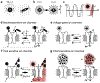
References
-
- Abraham J-A, Linnartz C, Dreissen G, Springer R, Blaschke S, et al. 2018. Directing neuronal outgrowth and network formation of rat cortical neurons by cyclic substrate stretch. Langmuir - PubMed
-
- Amstad E, Kohlbrecher J, Müller E, Schweizer T, Textor M, Reimhult E. 2011. Triggered Release from Liposomes through Magnetic Actuation of Iron Oxide Nanoparticle Containing Membranes. Nano Lett. 11: 1664–70 - PubMed
-
- Bean CP, Livingston JD. 1959. Superparamagnetism. J. Appl. Phys. 30: S120–S29
-
- Bergmann TO, Karabanov A, Hartwigsen G, Thielscher A, Siebner HR. 2016. Combining non-invasive transcranial brain stimulation with neuroimaging and electrophysiology: Current approaches and future perspectives. NeuroImage 140: 4–19 - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Medical

