Comparative Transcriptome Analysis of Ampelopsis megalophylla for Identifying Genes Involved in Flavonoid Biosynthesis and Accumulation during Different Seasons
- PMID: 30939828
- PMCID: PMC6480179
- DOI: 10.3390/molecules24071267
Comparative Transcriptome Analysis of Ampelopsis megalophylla for Identifying Genes Involved in Flavonoid Biosynthesis and Accumulation during Different Seasons
Abstract
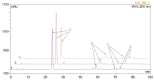
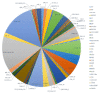
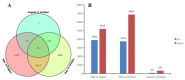
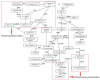
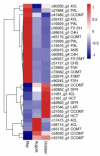
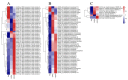
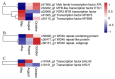
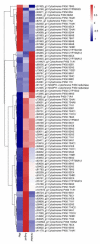
Ampelopsis megalophylla is an important species used in Chinese folk medicine. Flavonoids, the most important active components of plants, greatly determine the quality of A. megalophylla. However, biosynthesis of flavonoids at the molecular and genetic levels in A. megalophylla is not well understood. In this study, we performed chemical analysis and transcriptome analysis of A. megalophylla in different seasons (i.e., May, August, and October). Accumulation of flavonoids was higher in May than in the other two months. Genes involved in the flavonoid biosynthesis pathway, such as chalcone synthase, anthocyanidin synthase, flavanone 3-hydroxylase, flavonoid-3',5'-hydroxylase, caffeoyl-CoA O-methyltransferase, dihydroflavonol 4-reductase, 4-coumarate-CoA ligase, phenylalanine ammonia-lyase, cinnamate 4-hydroxylase, flavonoid 3'-monooxygenase, shikimate O-hydroxycinnamoyltransferase, and leucoanthocyanidin reductase, were identified based on transcriptome data. Fifty ATP binding cassette (ABC) transporter, nine SNARE, forty-nine GST, and eighty-four glycosyltransferases unigenes related to flavonoid transport and biomodification were also found. Moreover, seventy-eight cytochrome P450s and multiple transcription factors (five MYB, two bHLH, and three WD40 family genes) may be associated with the regulation of the flavonoid biosynthesis process. These results provide insights into the molecular processes of flavonoid biosynthesis in A. megalophylla and offer a significant resource for the application of genetic engineering in developing varieties with improved quality.
Keywords: Ampelopsis megalophylla; flavonoid accumulation; flavonoid biosynthesis; transcriptome.
Conflict of interest statement
The authors declare no conflict of interest.
Figures



References
-
- Chen M.L., Chen X.J., Li G., Zhang X.Q. Ampelopsis megalophylla ethanol extract of experimental studies on inhibition effect on expression of HBsAg, HBeAg 2215 cells. Chin. J. Tradit. Med. Sci. Technol. 2014;19:329–330.
-
- Yang R.J., Chen X.J., He X.Y., Rao R., Zhang X.Q., Liu Y.W. Study on anti-HBV virus effect of petroleum ether extracts of Ampelopsis megalophylla in vitro. Lishizhen Med. Materia Med. Res. 2011;22:153–215.
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Research Materials

