Initial experience and one-year follow-up with Neuroform Atlas Stent System for the treatment of brain aneurysms
- PMID: 30939955
- PMCID: PMC6777111
- DOI: 10.1177/1591019918819087
Initial experience and one-year follow-up with Neuroform Atlas Stent System for the treatment of brain aneurysms
Abstract
Introduction: The Neuroform Atlas Stent System is a recently introduced modification of the original Neuroform Stent System consisting of a hybrid design with open and closed cells. Initial experience, technical considerations and treatment outcomes including 1-year follow-up using the Atlas stent in combination with coil embolization are reported.
Material and methods: Thirty patients with 30 unruptured aneurysms were treated with stent reconstruction. Immediate, 4-month and 12-month post-treatment angiography and clinical assessment were performed.
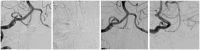
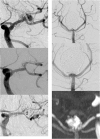
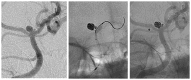
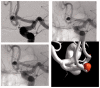
Discussion: In 29 cases, the stents were delivered and positioned without difficulty in deployment. Technical complications occurred in one patient related to advancement of the stent during delivery. One procedure-related clinical complication occurred with no permanent neurological deficit. On immediate post-treatment angiography, 29 of 30 aneurysms showed Raymond Class I or Class II occlusion. At 1-year follow-up, all 30 patients were clinically stable and 18 of 30 aneurysms showed Raymond Class I complete occlusion. Retreatment was performed in two patients with residual aneurysm.
Conclusions: The Atlas stent is technically safe and simple to implant and has a low thrombogenic potential. We experienced fewer problems associated with deployment and implantation, thromboembolic complications and hemorrhagic events compared with other types of stents, including braided stents. However, because of its low thrombogenic potential, partially occluded aneurysms or those with aneurysm remnants do not progress to complete occlusion.
Keywords: Aneurysm; brain; hemorrhage; stent; stroke.
Figures


References
-
- Molyneux A, Kerr R, Stratton I, et al. International Subarachnoid Aneurysm Trial (ISAT) of neurosurgical clipping versus endovascular coiling in 2143 patients with ruptured intracranial aneurysms: a randomised trial. Lancet 2002; 360: 1267–1274. - PubMed
-
- Molyneux AJ, Kerr RSC, Birks J, et al. Risk of recurrent subarachnoid haemorrhage, death, or dependence and standardised mortality ratios after clipping or coiling of an intracranial aneurysm in the International Subarachnoid Aneurysm Trial (ISAT): long-term follow-up. Lancet Neurol 2009; 8: 427–433. - PMC - PubMed
-
- Cognard C, Pierot L, Anxionnat R, et al. Results of embolization used as the first treatment choice in a consecutive nonselected population of ruptured aneurysms: clinical results of the Clarity GDC study. Neurosurgery 2011; 69: 837–841. - PubMed
-
- Pierot L, Cognard C, Anxionnat R, et al. Ruptured intracranial aneurysms: factors affecting the rate and outcome of endovascular treatment complications in a series of 782 patients (CLARITY study). Radiology 2010; 256: 916–923. - PubMed
MeSH terms
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Medical

