Phase 1 Study Evaluating the Association of the Cyclin-Dependent Kinase 4/6 Inhibitor Ribociclib and Cetuximab in Recurrent/Metastatic p16-Negative Squamous Cell Carcinoma of the Head and Neck
- PMID: 30941307
- PMCID: PMC6433958
- DOI: 10.3389/fonc.2019.00155
Phase 1 Study Evaluating the Association of the Cyclin-Dependent Kinase 4/6 Inhibitor Ribociclib and Cetuximab in Recurrent/Metastatic p16-Negative Squamous Cell Carcinoma of the Head and Neck
Abstract
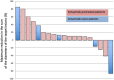
Background: The majority of human papillomavirus (HPV)-negative squamous cell carcinoma of the head and neck (SCCHN) present upregulation of the epidermal growth factor receptor (EGFR) and frequent alterations in the cyclin D1-cyclin dependent kinase (CDK) 4/6 (CDK 4/6)-retinoblastoma protein (pRb) pathway, resulting in cell cycle progression and tumor proliferation. This study investigated the combination of ribociclib, an orally highly selective inhibitor of CDK 4/6, and cetuximab in recurrent and/or metastatic (R/M) SCCHN. Methods: A phase I trial using a 3 + 3 design was performed to determine the dose limiting toxicity (DLT) and maximum tolerated dose (MTD) of ribociclib with standard dose of weekly cetuximab in HPV-negative patients with R/M SCCHN. Ribociclib was administered orally (3 weeks on/1 week off) at dose level 1 of 400 mg daily and dose level 2 of 600 mg daily. The MTD of ribocilib was then further evaluated in an expansion cohort. Results: 10 patients were enrolled in the escalation trial. No DLTs were observed at dose level 1 (n = 3); at dose level 2, one patient was replaced due to rapid disease progression, and one patient out of six evaluable patients experienced a DLT (grade 4 thrombocytopenia >7 days). Ribociclib 600 mg daily was thus determined to be the MTD. Eleven additional patients were enrolled in the expansion cohort. Diarrhea (52%), rash (52%), fatigue (43%), nausea (33%), and mucositis (28%) were the most frequent grade 1-2 adverse events (AE). Neutropenia was the most frequent grade 3-4 AE (20%). Median progression-free survival (PFS) was 3.5 months (range 0.4-17.3 months) and median overall survival (OS) was 8.3 months (range 0.4-24.1 months). Among the 19 radiologically evaluable patients, two (10.5%) achieved a partial response and 11 (58%) had stable disease. Conclusions: The MTD of ribociclib is 600 mg daily when administered in combination with standard dose cetuximab for 3 weeks on and 1 week off. This combination was safe and showed efficacy. Further clinical trials should be conducted to evaluate the antitumor effects of this combination. Trial Information: ClinicalTrials.gov: NCT02429089; Eudract number 2014-005371-83.
Keywords: HPV; cetuximab; head and neck; recurrent; ribociclib; squamous cell carcinoma.
Figures
References
-
- Bentzen SM, Atasoy BM, Daley FM, Dische S, Richman PI, Saunders MI, et al. . Epidermal growth factor receptor expression in pretreatment biopsies from head and neck squamous cell carcinoma as a predictive factor for a benefit from accelerated radiation therapy in a randomized controlled trial. J Clin Oncol. (2005) 23:5560–7. 10.1200/JCO.2005.06.411 - DOI - PubMed
Associated data
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Medical
Research Materials
Miscellaneous