A systematic review of just-in-time adaptive interventions (JITAIs) to promote physical activity
- PMID: 30943983
- PMCID: PMC6448257
- DOI: 10.1186/s12966-019-0792-7
A systematic review of just-in-time adaptive interventions (JITAIs) to promote physical activity
Abstract
Background: Progress in mobile health (mHealth) technology has enabled the design of just-in-time adaptive interventions (JITAIs). We define JITAIs as having three features: behavioural support that directly corresponds to a need in real-time; content or timing of support is adapted or tailored according to input collected by the system since support was initiated; support is system-triggered. We conducted a systematic review of JITAIs for physical activity to identify their features, feasibility, acceptability and effectiveness.
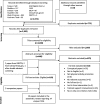
Methods: We searched Scopus, Medline, Embase, PsycINFO, Web of Science, DBLP, ACM Digital Library, Cochrane Central Register of Controlled Trials, ClinicalTrials.gov and the ISRCTN register using terms related to physical activity, mHealth interventions and JITAIs. We included primary studies of any design reporting data about JITAIs, irrespective of population, age and setting. Outcomes included physical activity, engagement, uptake, feasibility and acceptability. Paper screening and data extraction were independently validated. Synthesis was narrative. We used the mHealth Evidence Reporting and Assessment checklist to assess quality of intervention descriptions.
Results: We screened 2200 titles, 840 abstracts, 169 full-text papers, and included 19 papers reporting 14 unique JITAIs, including six randomised studies. Five JITAIs targeted both physical activity and sedentary behaviour, five sedentary behaviour only, and four physical activity only. JITAIs prompted breaks following sedentary periods and/or suggested physical activities during opportunistic moments, typically over three to four weeks. Feasibility challenges related to the technology, sensor reliability and timeliness of just-in-time messages. Overall, participants found JITAIs acceptable. We found mixed evidence for intervention effects on behaviour, but no study was sufficiently powered to detect any effects. Common behaviour change techniques were goal setting (behaviour), prompts/cues, feedback on behaviour and action planning. Five studies reported a theory-base. We found lack of evidence about cost-effectiveness, uptake, reach, impact on health inequalities, and sustained engagement.
Conclusions: Research into JITAIs to increase physical activity and reduce sedentary behaviour is in its early stages. Consistent use and a shared definition of the term 'JITAI' will aid evidence synthesis. We recommend robust evaluation of theory and evidence-based JITAIs in representative populations. Decision makers and health professionals need to be cautious in signposting patients to JITAIs until such evidence is available, although they are unlikely to cause health-related harm.
Reference: PROSPERO 2017 CRD42017070849.
Keywords: Digital intervention; Exercise; Just-in-time Adaptive Intervention; Mobile Health; Mobile applications; Physical activity; Sedentary behaviour; Telemedicine.
Conflict of interest statement
Ethics approval and consent to participate
Not applicable.
Consent for publication
Not applicable.
Competing interests
The authors declare that they have no competing interests
Publisher’s Note
Springer Nature remains neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations.
Figures
References
-
- World Health Organization. mHealth: new horizons for health through mobile technologies: second global survey on eHealth. http://www.who.int/goe/publications/goe_mhealth_web.pdf (Accessed 19 Dec 2018). 2011.
-
- Direito A, Carraca E, Rawstorn J, Whittaker R, Maddison R. mHealth technologies to influence physical activity and sedentary behaviors: behavior change techniques, systematic review and meta-analysis of randomized controlled trials. Ann Behav Med. 2017;51(2):226–239. doi: 10.1007/s12160-016-9846-0. - DOI - PubMed