NKG2A is a NK cell exhaustion checkpoint for HCV persistence
- PMID: 30944315
- PMCID: PMC6447531
- DOI: 10.1038/s41467-019-09212-y
NKG2A is a NK cell exhaustion checkpoint for HCV persistence
Abstract
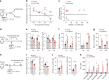
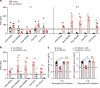
Exhaustion of cytotoxic effector natural killer (NK) and CD8+ T cells have important functions in the establishment of persistent viral infections, but how exhaustion is induced during chronic hepatitis C virus (HCV) infection remains poorly defined. Here we show, using the humanized C/OTg mice permissive for persistent HCV infection, that NK and CD8+ T cells become sequentially exhausted shortly after their transient hepatic infiltration and activation in acute HCV infection. HCV infection upregulates Qa-1 expression in hepatocytes, which ligates NKG2A to induce NK cell exhaustion. Antibodies targeting NKG2A or Qa-1 prevents NK exhaustion and promotes NK-dependent HCV clearance. Moreover, reactivated NK cells provide sufficient IFN-γ that helps rejuvenate polyclonal HCV CD8+ T cell response and clearance of HCV. Our data thus show that NKG2A serves as a critical checkpoint for HCV-induced NK exhaustion, and that NKG2A blockade sequentially boosts interdependent NK and CD8+ T cell functions to prevent persistent HCV infection.
Conflict of interest statement
The authors declare no competing interests.
Figures





Comment in
-
Functional exhaustion of antiviral lymphocytes in COVID-19 patients.Cell Mol Immunol. 2020 May;17(5):533-535. doi: 10.1038/s41423-020-0402-2. Epub 2020 Mar 19. Cell Mol Immunol. 2020. PMID: 32203188 Free PMC article. No abstract available.
References
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Molecular Biology Databases
Research Materials
Miscellaneous

