Trends in cause-specific mortality in HIV-hepatitis C coinfection following hepatitis C treatment scale-up
- PMID: 30946155
- PMCID: PMC6467558
- DOI: 10.1097/QAD.0000000000002156
Trends in cause-specific mortality in HIV-hepatitis C coinfection following hepatitis C treatment scale-up
Abstract
Objective: Hepatitis C virus (HCV) treatment may reduce liver-related mortality but with competing risks, other causes of mortality may undermine benefits. We examined changes in cause-specific mortality among HIV-HCV coinfected patients before and after scale-up of HCV treatment.
Design: Prospective multicentre HIV-HCV cohort study in Canada.
Methods: Cause-specific deaths, classified using a modified 'Coding of Cause of Death in HIV' protocol, were determined for two time periods, 2003-2012 and 2013-2017, stratified by age (20-49; 50-80 years). Comparison of trends between periods was performed using Poisson regression. To account for competing risks, multinomial regression was used to estimate the cause-specific hazard ratios of time and age on cause of death, from which end-stage liver disease (ESLD)-specific 5-year cumulative incidence functions were estimated.
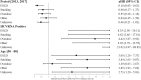
Results: Overall, 1634 participants contributed 8248 person-years of follow-up; 273 (17%) died. Drug overdose was the most common cause of death overall, followed by ESLD and smoking-related deaths. In 2013-2017, ESLD was surpassed by drug overdose and smoking-related deaths among those aged 20-49 and 50-80, respectively. After accounting for competing risks, comparing 2003-2012 to 2013-2017, ESLD deaths declined (adjusted hazards ratio: 0.18, 95% confidence interval 0.05-0.62). However, both early and late period cumulative incidence functions demonstrated increased risk of death from ESLD for patients with poor HIV control and advanced fibrosis.
Conclusion: The gains made in overall mortality with HCV therapy may be thwarted if modifiable harms are not addressed. Although ESLD-related deaths have decreased over time, treatment should be further expanded, prioritizing those with advanced fibrosis.
Figures


References
-
- Palella FJ, Jr, Delaney KM, Moorman AC, Loveless MO, Fuhrer J, Satten GA, et al. Declining morbidity and mortality among patients with advanced human immunodeficiency virus infection. HIV Outpatient Study Investigators. N Engl J Med 1998; 338:853–860. - PubMed
-
- Mocroft A, Ledergerber B, Katlama C, Kirk O, Reiss P, d’Arminio Monforte A, et al. Decline in the AIDS and death rates in the EuroSIDA study: an observational study. Lancet 2003; 362:22–29. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Medical

