Location is the key to function: HMGB1 in sepsis and trauma-induced inflammation
- PMID: 30946496
- PMCID: PMC6597316
- DOI: 10.1002/JLB.3MIR1218-497R
Location is the key to function: HMGB1 in sepsis and trauma-induced inflammation
Abstract
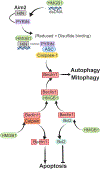
High mobility group box 1 (HMGB1) is a multifunctional nuclear protein, probably known best as a prototypical alarmin or damage-associated molecular pattern (DAMP) molecule when released from cells. However, HMGB1 has multiple functions that depend on its location in the nucleus, in the cytosol, or extracellularly after either active release from cells, or passive release upon lytic cell death. Movement of HMGB1 between cellular compartments is a dynamic process induced by a variety of cell stresses and disease processes, including sepsis, trauma, and hemorrhagic shock. Location of HMGB1 is intricately linked with its function and is regulated by a series of posttranslational modifications. HMGB1 function is also regulated by the redox status of critical cysteine residues within the protein, and is cell-type dependent. This review highlights some of the mechanisms that contribute to location and functions of HMGB1, and focuses on some recent insights on important intracellular effects of HMGB1 during sepsis and trauma.
Keywords: AIM2; DAMPs; autophagy; caspase-11; pyroptosis.
©2019 Society for Leukocyte Biology.
Conflict of interest statement
Conflict of Interest
The authors declare no conflicts of interest.
Figures
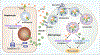
References
-
- Einck L and Bustin M (1985) The intracellular distribution and function of the high mobility group chromosomal proteins. Exp Cell Res 156, 295–310. - PubMed
-
- Javaherian K, Liu JF, Wang JC (1978) Nonhistone proteins HMG1 and HMG2 change the DNA helical structure. Science 199, 1345–6. - PubMed
-
- Ferrari S, Ronfani L, Calogero S, Bianchi ME (1994) The mouse gene coding for high mobility group 1 protein (HMG1). J Biol Chem 269, 28803–8. - PubMed
-
- Gariboldi M, De Gregorio L, Ferrari S, Manenti G, Pierotti MA, Bianchi ME, Dragani TA (1995) Mapping of the Hmg1 gene and of seven related sequences in the mouse. Mamm Genome 6, 581–5. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Medical

