Obstructive Sleep Apnea and the Liver
- PMID: 30947882
- PMCID: PMC6591731
- DOI: 10.1016/j.cld.2019.01.001
Obstructive Sleep Apnea and the Liver
Abstract
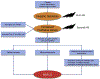
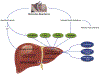
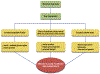
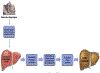
Nonalcoholic fatty liver disease (NAFLD), a disorder of altered metabolic pathways, is increasing worldwide. Recent studies established obstructive sleep apnea (OSA) and chronic intermittent hypoxia (CIH) as NAFLD risk factors. Studies have ascertained that CIH is independently related to NAFLD. Continuous positive airway pressure (CPAP) shows inconsistent results regarding its efficacy in improving NAFLD. Observational, longer duration CPAP therapy studies have shown positive outcomes, whereas shorter duration, randomized controlled trials have shown no benefit. A multifaceted approach to NAFLD management with sufficiently longer duration of CPAP therapy may be beneficial in patients with moderate to severe OSA.
Keywords: Chronic intermittent hypoxia and insulin resistance; Hepatic steatosis; Nonalcoholic fatty liver disease; Obstructive sleep apnea.
Copyright © 2019 Elsevier Inc. All rights reserved.
Figures
References
-
- Ratziu V, Bellentani S, Cortez-Pinto H, et al. A position statement on NAFLD/NASH based on the EASL 2009 special conference. J Hepatol 2010;53:372–84. - PubMed
-
- Angulo P Nonalcoholic fatty liver disease. N Engl J Med 2002;346:1221–31. - PubMed
-
- Younossi ZM, Koenig AB, Abdelatif D, et al. Global epidemiology of nonalcoholic fatty liver disease-Meta-analytic assessment of prevalence, incidence, and outcomes. Hepatology 2016;64(1):73–84. - PubMed
-
- Anstee QM, Targher G, Day CP. Progression of NAFLD to diabetes mellitus, cardiovascular disease or cirrhosis. Nat Rev Gastroenterol Hepatol 2013;10: 330–44. - PubMed
-
- Parikh ND, Marrero WJ, Wang J, et al. Projected increase in obesity and non-alcoholic-steatohepatitis-related liver transplantation waitlist additions in the United States. Hepatology 2017. [Epub ahead of print]. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Medical