Placental growth factor testing to assess women with suspected pre-eclampsia: a multicentre, pragmatic, stepped-wedge cluster-randomised controlled trial
- PMID: 30948284
- PMCID: PMC6497988
- DOI: 10.1016/S0140-6736(18)33212-4
Placental growth factor testing to assess women with suspected pre-eclampsia: a multicentre, pragmatic, stepped-wedge cluster-randomised controlled trial
Abstract
Background: Previous prospective cohort studies have shown that angiogenic factors have a high diagnostic accuracy in women with suspected pre-eclampsia, but we remain uncertain of the effectiveness of these tests in a real-world setting. We therefore aimed to determine whether knowledge of the circulating concentration of placental growth factor (PlGF), an angiogenic factor, integrated with a clinical management algorithm, decreased the time for clinicians to make a diagnosis in women with suspected pre-eclampsia, and whether this approach reduced subsequent maternal or perinatal adverse outcomes.
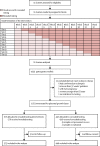
Methods: We did a multicentre, pragmatic, stepped-wedge cluster-randomised controlled trial in 11 maternity units in the UK, which were each responsible for 3000-9000 deliveries per year. Women aged 18 years and older who presented with suspected pre-eclampsia between 20 weeks and 0 days of gestation and 36 weeks and 6 days of gestation, with a live, singleton fetus were invited to participate by the clinical research team. Suspected pre-eclampsia was defined as new-onset or worsening of existing hypertension, dipstick proteinuria, epigastric or right upper-quadrant pain, headache with visual disturbances, fetal growth restriction, or abnormal maternal blood tests that were suggestive of disease (such as thrombocytopenia or hepatic or renal dysfunction). Women were approached individually, they consented for study inclusion, and they were asked to give blood samples. We randomly allocated the maternity units, representing the clusters, to blocks. Blocks represented an intervention initiation time, which occurred at equally spaced 6-week intervals throughout the trial. At the start of the trial, all units had usual care (in which PlGF measurements were also taken but were concealed from clinicians and women). At the initiation time of each successive block, a site began to use the intervention (in which the circulating PlGF measurement was revealed and a clinical management algorithm was used). Enrolment of women continued for the duration of the blocks either to concealed PlGF testing, or after implementation, to revealed PlGF testing. The primary outcome was the time from presentation with suspected pre-eclampsia to documented pre-eclampsia in women enrolled in the trial who received a diagnosis of pre-eclampsia by their treating clinicians. This trial is registered with ISRCTN, number 16842031.
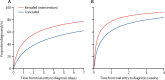
Findings: Between June 13, 2016, and Oct 27, 2017, we enrolled and assessed 1035 women with suspected pre-eclampsia. 12 (1%) women were found to be ineligible. Of the 1023 eligible women, 576 (56%) women were assigned to the intervention (revealed testing) group, and 447 (44%) women were assigned to receive usual care with additional concealed testing (concealed testing group). Three (1%) women in the revealed testing group were lost to follow-up, so 573 (99%) women in this group were included in the analyses. One (<1%) woman in the concealed testing group withdrew consent to follow-up data collection, so 446 (>99%) women in this group were included in the analyses. The median time to pre-eclampsia diagnosis was 4·1 days with concealed testing versus 1·9 days with revealed testing (time ratio 0·36, 95% CI 0·15-0·87; p=0·027). Maternal severe adverse outcomes were reported in 24 (5%) of 447 women in the concealed testing group versus 22 (4%) of 573 women in the revealed testing group (adjusted odds ratio 0·32, 95% CI 0·11-0·96; p=0·043), but there was no evidence of a difference in perinatal adverse outcomes (15% vs 14%, 1·45, 0·73-2·90) or gestation at delivery (36·6 weeks vs 36·8 weeks; mean difference -0·52, 95% CI -0·63 to 0·73).
Interpretation: We found that the availability of PlGF test results substantially reduced the time to clinical confirmation of pre-eclampsia. Where PlGF was implemented, we found a lower incidence of maternal adverse outcomes, consistent with adoption of targeted, enhanced surveillance, as recommended in the clinical management algorithm for clinicians. Adoption of PlGF testing in women with suspected pre-eclampsia is supported by the results of this study.
Funding: National Institute for Health Research.
Copyright © 2019 The Author(s). Published by Elsevier Ltd. This is an Open Access article under the CC BY 4.0 license. Published by Elsevier Ltd.. All rights reserved.
Figures
Comment in
-
Pembrolizumab for all PD-L1-positive NSCLC.Lancet. 2019 May 4;393(10183):1776-1778. doi: 10.1016/S0140-6736(18)32559-5. Epub 2019 Apr 4. Lancet. 2019. PMID: 30955976 No abstract available.
-
Placental growth factor testing for suspected pre-eclampsia.Lancet. 2019 May 4;393(10183):1775-1776. doi: 10.1016/S0140-6736(19)30958-4. Lancet. 2019. PMID: 31057150 No abstract available.
-
Placental growth factor testing to assess women with suspected pre-eclampsia.BMJ Evid Based Med. 2020 Apr;25(2):73-74. doi: 10.1136/bmjebm-2019-111228. Epub 2019 Jul 3. BMJ Evid Based Med. 2020. PMID: 31270146 No abstract available.
-
Time to speed up the diagnosis of pre-eclampsia.Drug Ther Bull. 2019 Aug;57(8):114. doi: 10.1136/dtb.2019.000024. Drug Ther Bull. 2019. PMID: 31345955 No abstract available.
-
Placental growth factor testing in suspected pre-eclampsia.Lancet. 2020 Feb 1;395(10221):335. doi: 10.1016/S0140-6736(19)32496-1. Lancet. 2020. PMID: 32007161 No abstract available.
-
Placental growth factor testing in suspected pre-eclampsia.Lancet. 2020 Feb 1;395(10221):335-336. doi: 10.1016/S0140-6736(19)32566-8. Lancet. 2020. PMID: 32007162 No abstract available.
References
-
- Duley L. The global impact of pre-eclampsia and eclampsia. Semin Perinatol. 2009;33:130–137. - PubMed
-
- Tan MY, Wright D, Syngelaki A. Comparison of diagnostic accuracy of early screening for pre-eclampsia by NICE guidelines and a method combining maternal factors and biomarkers: results of SPREE. Ultrasound Obstet Gynecol. 2018;51:743–750. - PubMed
-
- Villar J, Repke J, Markush L, Calvert W, Rhoads G. The measuring of blood pressure during pregnancy. Am J Obstet Gynecol. 1989;161:1019–1024. - PubMed
-
- Durnwald C, Mercer B. A prospective comparison of total protein/creatinine ratio versus 24-hour urine protein in women with suspected preeclampsia. Am J Obstet Gynecol. 2003;189:848–852. - PubMed
-
- Waugh J, Bell SC, Kilby MD, Lambert P, Shennan A, Halligan A. Urine protein estimation in hypertensive pregnancy: which thresholds and laboratory assay best predict clinical outcome? Hypertens Pregnancy. 2005;24:291–302. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Medical