Shieldin - the protector of DNA ends
- PMID: 30948458
- PMCID: PMC6501030
- DOI: 10.15252/embr.201847560
Shieldin - the protector of DNA ends
Abstract
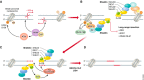
DNA double-strand breaks are a threat to genome integrity and cell viability. The nucleolytic processing of broken DNA ends plays a central role in dictating the repair processes that will mend these lesions. Usually, DNA end resection promotes repair by homologous recombination, whereas minimally processed ends are repaired by non-homologous end joining. Important in this process is the chromatin-binding protein 53BP1, which inhibits DNA end resection. How 53BP1 shields DNA ends from nucleases has been an enduring mystery. The recent discovery of shieldin, a four-subunit protein complex with single-stranded DNA-binding activity, illuminated a strong candidate for the ultimate effector of 53BP1-dependent end protection. Shieldin consists of REV7, a known 53BP1-pathway component, and three hitherto uncharacterized proteins: C20orf196 (SHLD1), FAM35A (SHLD2), and CTC-534A2.2 (SHLD3). Shieldin promotes many 53BP1-associated activities, such as the protection of DNA ends, non-homologous end joining, and immunoglobulin class switching. This review summarizes the identification of shieldin and the various models of shieldin action and highlights some outstanding questions requiring answers to gain a full molecular understanding of shieldin function.
Keywords: DNA repair; end resection; genome stability; homologous recombination; non‐homologous end joining.
© 2019 The Authors.
Conflict of interest statement
DS has no conflict of interest to declare; DD declares that he is a founder and shareholder of Repare Therapeutics.
Figures


References
-
- Panier S, Boulton SJ (2014) Double‐strand break repair: 53BP1 comes into focus. Nat Rev Mol Cell Biol 15: 7–18 - PubMed
-
- Nakamura K, Sakai W, Kawamoto T, Bree RT, Lowndes NF, Takeda S, Taniguchi Y (2006) Genetic dissection of vertebrate 53BP1: a major role in non‐homologous end joining of DNA double strand breaks. DNA Repair 5: 741–749 - PubMed
-
- Manis JP, Morales JC, Xia Z, Kutok JL, Alt FW, Carpenter PB (2004) 53BP1 links DNA damage‐response pathways to immunoglobulin heavy chain class‐switch recombination. Nat Immunol 5: 481–487 - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources

