Dephosphorylation of the transcriptional cofactor NACA by the PP1A phosphatase enhances cJUN transcriptional activity and osteoblast differentiation
- PMID: 30948508
- PMCID: PMC6527172
- DOI: 10.1074/jbc.RA118.006920
Dephosphorylation of the transcriptional cofactor NACA by the PP1A phosphatase enhances cJUN transcriptional activity and osteoblast differentiation
Abstract
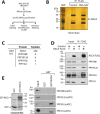
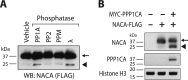
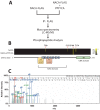
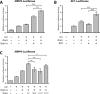
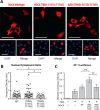
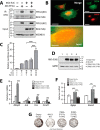
The transcriptional cofactor nascent polypeptide-associated complex and co-regulator α (NACA) regulates osteoblast maturation and activity. NACA functions, at least in part, by binding to Jun proto-oncogene, AP-1 transcription factor subunit (cJUN) and potentiating the transactivation of AP-1 targets such as osteocalcin (Bglap) and matrix metallopeptidase 9 (Mmp9). NACA activity is modulated by phosphorylation carried out by several kinases, but a phosphatase regulating NACA's activity remains to be identified. Here, we used affinity purification with MS in HEK293T cells to isolate NACA complexes and identified protein phosphatase 1 catalytic subunit α (PP1A) as a NACA-associated Ser/Thr phosphatase. NACA interacted with multiple components of the PP1A holoenzyme complex: the PPP1CA catalytic subunit and the regulatory subunits PPP1R9B, PPP1R12A and PPP1R18. MS analysis revealed that NACA co-expression with PPP1CA causes dephosphorylation of NACA at Thr-89, Ser-151, and Thr-174. NACA Ser/Thr-to-alanine variants displayed increased nuclear localization, and NACA dephosphorylation was associated with specific recruitment of novel NACA interactants, such as basic transcription factor 3 (BTF3) and its homolog BTF3L4. NACA and PP1A cooperatively potentiated cJUN transcriptional activity of the AP-1-responsive MMP9-luciferase reporter, which was abolished when Thr-89, Ser-151, or Thr-174 were substituted with phosphomimetic aspartate residues. We confirmed the NACA-PP1A interaction in MC3T3-E1 osteoblastic cells and observed that NACA phosphorylation status at PP1A-sensitive sites is important for the regulation of AP-1 pathway genes and for osteogenic differentiation and matrix mineralization. These results suggest that PP1A dephosphorylates NACA at specific residues, impacting cJUN transcriptional activity and osteoblast differentiation and function.
Keywords: AP1 transcription factor (AP-1); JUN, transcription; PP1A; Protein phosphatase 1 catalytic subunit alpha (PP1A); c-Jun transcription factor; cell differentiation; cell signaling; nascent polypeptide-associated complex and co-regulator alpha (NACA); osteoblast; phosphatase; αNAC.
© 2019 Addison et al.
Conflict of interest statement
The authors declare that they have no conflicts of interest with the contents of this article
Figures

References
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Molecular Biology Databases
Miscellaneous

