Esophageal diverticulum: New perspectives in the era of minimally invasive endoscopic treatment
- PMID: 30948909
- PMCID: PMC6441918
- DOI: 10.3748/wjg.v25.i12.1457
Esophageal diverticulum: New perspectives in the era of minimally invasive endoscopic treatment
Abstract
Esophageal diverticula are rare conditions that cause esophageal symptoms, such as dysphagia, regurgitation, and chest pain. They are classified according to their location and characteristic pathophysiology into three types: epiphrenic diverticulum, Zenker's diverticulum, and Rokitansky diverticulum. The former two disorders take the form of protrusions, and symptomatic cases require interventional treatment. However, the esophageal anatomy presents distinct challenges to surgical resection of the diverticulum, particularly when it is located closer to the oral orifice. Since the condition itself is not malignant, minimally invasive endoscopic approaches have been developed with a focus on alleviation of symptoms. Several types of endoscopic devices and techniques are currently employed, including peroral endoscopic myotomy (POEM). However, the use of minimally invasive endoscopic approaches, like POEM, has allowed the development of new disorder called iatrogenic esophageal diverticula. In this paper, we review the pathophysiology of each type of diverticulum and the current state-of-the-art treatment based on our experience.
Keywords: Diverticulectomy; Diverticulum; Epiphrenic diverticulum; Esophageal achalasia; Esophagus; Iatrogenic disease; Peroral endoscopic myotomy; Rokitansky diverticulum; Zenker’s diverticulum.
Conflict of interest statement
Conflict-of-interest statement: No potential conflicts of interest.
Figures

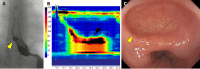

References
-
- Soares R, Herbella FA, Prachand VN, Ferguson MK, Patti MG. Epiphrenic diverticulum of the esophagus. From pathophysiology to treatment. J Gastrointest Surg. 2010;14:2009–2015. - PubMed
-
- Tedesco P, Fisichella PM, Way LW, Patti MG. Cause and treatment of epiphrenic diverticula. Am J Surg. 2005;190:891–894. - PubMed
-
- Melman L, Quinlan J, Robertson B, Brunt LM, Halpin VJ, Eagon JC, Frisella MM, Matthews BD. Esophageal manometric characteristics and outcomes for laparoscopic esophageal diverticulectomy, myotomy, and partial fundoplication for epiphrenic diverticula. Surg Endosc. 2009;23:1337–1341. - PubMed
-
- Del Genio A, Rossetti G, Maffetton V, Renzi A, Brusciano L, Limongelli P, Cuttitta D, Russo G, Del Genio G. Laparoscopic approach in the treatment of epiphrenic diverticula: long-term results. Surg Endosc. 2004;18:741–745. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Medical

