Emerging Trends and New Developments in Transient Elastography: A Bibliometric and Cocitation Analysis from 1999 to 2017
- PMID: 30949458
- PMCID: PMC6425420
- DOI: 10.1155/2019/3280657
Emerging Trends and New Developments in Transient Elastography: A Bibliometric and Cocitation Analysis from 1999 to 2017
Abstract
Purpose: To identify and characterize the 100 most-cited articles in the field of transient elastography.
Methods: The top-cited articles focusing on transient elastography from 1999 to 2017 were retrieved from Science Citation Index Expanded (SCI-E) database. The most prolific article, journal, country and continent, top-cited article in different period, international collaboration, cocitation analysis of journal were retrieved and analyzed in this article. Bibexcel 2016, Microsoft Excel 2010, and VOSviewer 1.6.5 were used to analyze bibliometric records we downloaded.
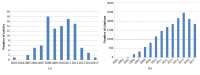
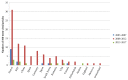
Results: The 100 most-cited articles were published between 2003 and 2015. The total citations ranged from 54 to 1376 (mean, 167.52 ± 208.46; median, 89.5) and the annual citations ranged from 4.91 to 98.24 (mean, 17.21±15.68; median, 12.1). The top-cited article was published in Gastroenterology in 2005 by Castera L. et al. (n=1376). The most-cited articles in 2003-2007 (n=1380), 2008-2012 (n=599) and 2013-2017 (n=159) were located. All of the most-cited articles in three periods were focusing on the topic of noninvasive assessment of liver fibrosis. The most prolific author was de Ledinghen V. (n=21) and France (n=43) was the leading country. The most productive journal was Journal of Hepatology (n=20). The major article type was original research article.
Conclusions: We undertook efforts to provide an insight into the features and evolvement of the most-cited articles in the field of transient elastography. For transient elastography, as a noninvasive assessment of liver fibrosis, its use in the evaluation of liver fibrosis is gradually mature and shows great advantages. Moreover, the field of transient elastography is in a stage of rapid development.
Figures


References
MeSH terms
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Medical

