IFITM3 knockdown reduces the expression of CCND1 and CDK4 and suppresses the growth of oral squamous cell carcinoma cells
- PMID: 30949979
- PMCID: PMC7771307
- DOI: 10.1007/s13402-019-00437-z
IFITM3 knockdown reduces the expression of CCND1 and CDK4 and suppresses the growth of oral squamous cell carcinoma cells
Abstract
Purpose: Oral squamous cell carcinoma (OSCC) is a challenging disease to treat. Up to 50% of OSCC patients with advanced disease develop recurrences. Elucidation of key molecular mechanisms underlying OSCC development may provide opportunities to target specific genes and, thus, to improve patient survival. In this study, we examined the expression and functional role of interferon transmembrane protein 3 (IFITM3) in OSCC development.
Methods: The expression of IFITM3 in OSCC and normal oral mucosal tissues was assessed by qRT-PCR and immunohistochemistry. The role of IFITM3 in driving OSCC cell proliferation and survival was examined using siRNA-mediated gene knockdown, and the role of IFITM3 in driving cell cycle regulators was examined using Western blotting.
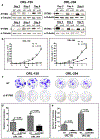
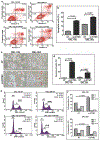
Results: We found that IFITM3 is overexpressed in more than 79% of primary OSCCs. We also found that IFITM3 knockdown led to impaired OSCC cell growth through inhibition of cell proliferation, induction of cell cycle arrest, senescence and apoptosis. In addition, we found that IFITM3 knockdown led to reduced expressions of CCND1 and CDK4 and reduced RB phosphorylation, leading to inhibition of OSCC cell growth. This information may be instrumental for the design of novel targeted therapeutic strategies.
Conclusions: From our data we conclude that IFITM3 is overexpressed in OSCC and may regulate the CCND1-CDK4/6-pRB axis to mediate OSCC cell growth.
Keywords: CCND1; CDK4; IFITM3; Oral squamous cell carcinoma; Proliferation.
Conflict of interest statement
Figures



References
-
- Martensen PM, Justesen J, Small ISGs coming forward. J Interf Cytokine Res 24, 1–19 (2004) - PubMed
-
- Siegrist F, Ebeling M, Certa U, The small interferon-induced transmembrane genes and proteins. J Interf Cytokine Res 31, 183–197 (2011) - PubMed
-
- Everitt AR, Clare S, Pertel T, John SP, Wash RS, Smith SE, Chin CR, Feeley EM, Sims JS, Adams DJ, Wise HM, Kane L, Goulding D, Digard P, Anttila V, Baillie JK, Walsh TS, Hume DA, Palotie A, Xue Y, Colonna V, Tyler-Smith C, Dunning J, Gordon SB, Smyth RL, Openshaw PJ, Dougan G, Brass AL, Kellam P, IFITM3 restricts the morbidity and mortality associated with influenza. Nature 484, 519–523 (2012) - PMC - PubMed
-
- Brass AL, Huang IC, Benita Y, John SP, Krishnan MN, Feeley EM, Ryan BJ, Weyer JL, van der Weyden L, Fikrig E, Adams DJ, Xavier RJ, Farzan M, Elledge SJ, The IFITM proteins mediate cellular resistance to influenza A H1N1 virus, West Nile virus, and dengue virus. Cell 139, 1243–1254 (2009) - PMC - PubMed
-
- Evans SS, Collea RP, Leasure JA, Lee DB, IFN-alpha induces homotypic adhesion and Leu-13 expression in human B lymphoid cells. J Immunol 150, 736–747 (1993) - PubMed
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Medical
Research Materials

