Ultrasonography for oxygen-ozone therapy in musculoskeletal diseases
- PMID: 30950416
- PMCID: PMC6463440
- DOI: 10.4103/2045-9912.254638
Ultrasonography for oxygen-ozone therapy in musculoskeletal diseases
Abstract
Over the years, infiltrative oxygen-ozone therapy has shown clinical benefits in several musculoskeletal disorders, due to its potential analgesic, anti-inflammatory, antioxidant and immunomodulatory effect. Ultrasonography is a safe, non-invasive imaging, easily available, and has the additional advantage of being real time for imaging and image-guided procedures of the musculoskeletal system. This review explains the numerous promising ways in which ultrasonography can be useful in oxygen-ozone therapeutic practices for musculoskeletal disorders, in order to improve safety and accuracy of treatment.
Keywords: intraaticular ozone; musculoskeletal diseases; oxygen-ozone therapy; ozone; paravertebral injection; peritendinous zone; ultrasonography; ultrasound.
Conflict of interest statement
None
Figures
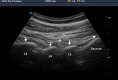

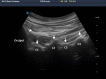
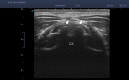
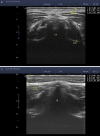
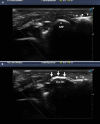
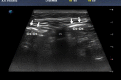
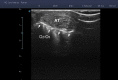
References
-
- Bocci V. How a calculated oxidative stress can yield multiple therapeutic effects. Free Radic Res. 2012;46:1068–1075. - PubMed
-
- Bocci V, Valacchi G. Free radicals and antioxidants: how to reestablish redox homeostasis in chronic diseases? Curr Med Chem. 2013;20:3397–3415. - PubMed
-
- Bocci V. Dordrechit: Kluwer Academic Publishers; 2002. Oxygen-Ozone Therapy: A Critical Evaluation.
-
- Bocci VA. Scientific and medical aspects of ozone therapy. State of the art. Arch Med Res. 2006;37:425–435. - PubMed
-
- Bocci V, Borrelli E, Travagli V, Zanardi I. The ozone paradox: ozone is a strong oxidant as well as a medical drug. Med Res Rev. 2009;29:646–682. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Medical

