Discovery of False Elite Controllers: HIV Antibody-Positive RNA-Negative Blood Donors Found To Be on Antiretroviral Therapy
- PMID: 30950501
- PMCID: PMC6639597
- DOI: 10.1093/infdis/jiz145
Discovery of False Elite Controllers: HIV Antibody-Positive RNA-Negative Blood Donors Found To Be on Antiretroviral Therapy
Abstract
Background: An increase in potential HIV elite controllers (EC) and anecdotal reports of antiretroviral therapy (ART) use among South African blood donors led us to verify EC status.
Methods: Stored plasma samples from potential EC were tested for ART drugs. Demographic and temporal associations were examined using multivariable logistic regression.
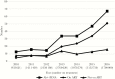
Results: Of 226 potential EC, 150 (66.4%) had detectable ART with increasing prevalence by year (OR = 7.57 for 2016 vs 2010, 95% confidence interval, 1.96-32.17).
Discussion: False presumptive EC status due to undisclosed ART represents a growing proportion of potential EC donors in South Africa coincident with the country's ART rollout.
Keywords: HIV; South Africa; antiretroviral therapy; blood donors; disclosure; elite controller.
© The Author(s) 2019. Published by Oxford University Press for the Infectious Diseases Society of America. All rights reserved. For permissions, e-mail: journals.permissions@oup.com.
Figures
References
-
- South African National AIDS Council. Let our actions count: Reflections on NSP 2012–2016 and moving forward to NSP 2017–2022. Pretoria, South Africa: SANAC, 2016.
-
- Deeks SG, Walker BD. Human immunodeficiency virus controllers: mechanisms of durable virus control in the absence of antiretroviral therapy. Immunity 2007; 27:406–16. - PubMed
-
- Grabarczyk P, van Drimmelen H, Kopacz A, et al. . Head-to-head comparison of two transcription-mediated amplification assay versions for detection of hepatitis B virus, hepatitis C virus, and human immunodeficiency virus type 1 in blood donors. Transfusion 2013; 53:2512–24. - PubMed

