Crystallization of the human tetraspanin protein CD9
- PMID: 30950826
- PMCID: PMC6450527
- DOI: 10.1107/S2053230X1801840X
Crystallization of the human tetraspanin protein CD9
Abstract
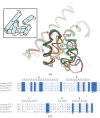
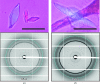
The tetraspanin family of proteins with four membrane-spanning proteins function in a wide range of physiological processes in higher organisms, including cell migration and proliferation, cell fusion, fertilization and virus infection. Although the recently reported structure of CD81 unveiled the basic architecture of this family for the first time, further structural and functional studies are required in order to understand the mechanistic details of the complicated functions of the tetraspanin-family proteins. In this study, attempts were made to crystallize human CD9, a representative member of the tetraspanin family, and it was demonstrated that the truncation of a variable region in the second long extracellular loop significantly improved crystal growth.
Keywords: CD9; LCP; crystallization; membrane proteins; tetraspanins.
open access.
Figures

References
-
- Charrin, S., Jouannet, S., Boucheix, C. & Rubinstein, E. (2014). J. Cell Sci. 127, 3641–3648. - PubMed
-
- Charrin, S., le Naour, F., Silvie, O., Milhiet, P.-E., Boucheix, C. & Rubinstein, E. (2009). Biochem. J. 420, 133–154. - PubMed
-
- Charrin, S., Manié, S., Oualid, M., Billard, M., Boucheix, C. & Rubinstein, E. (2002). FEBS Lett. 516, 139–144. - PubMed
-
- Hemler, M. E. (2003). Annu. Rev. Cell Dev. Biol. 19, 397–422. - PubMed
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources

