Antibody-mediated targeting of cleavage-specific OPN-T cell interactions
- PMID: 30951532
- PMCID: PMC6450625
- DOI: 10.1371/journal.pone.0214938
Antibody-mediated targeting of cleavage-specific OPN-T cell interactions
Abstract
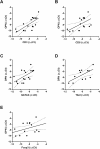
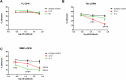
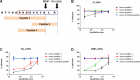
T cells are crucial players in obesity-mediated adipose tissue inflammation. We hypothesized that osteopontin (OPN), an inflammatory protein with enhanced activity when proteolytically cleaved, affects the number of viable T cells in adipose tissue and assessed inhibition of the interaction between T cells and thrombin and matrix metalloproteinases-cleaved OPN using antibodies and postimmune sera. Gene expression of T cell markers in adipose tissue from wild-type (wt) and Spp1-/- (OPN deficient) mice was analyzed after 16 weeks of high fat diet (HFD) or low fat diet (LFD) feeding. CD3, CD8 and OPN gene expression in omental adipose tissue from individuals with obesity was measured. OPN-T cell interactions were assessed with a fluorescence-based adhesion assay and blocked with antibodies targeting OPN. Comparison of T cell gene expression in adipose tissue from wt and Spp1-/- mice showed that OPN affected the number of T cells while in humans, levels of OPN correlated with T cell markers in omental adipose tissue. The interaction between T cells and cleaved OPN was blocked by postimmune sera following OPN peptide vaccinations and with monoclonal antibodies. In conclusion, levels of OPN affected the number of T cells in obesity and antibodies against cleaved OPN antagonize OPN-T cell interactions.
Conflict of interest statement
The author G. Staffler is employee of AFFiRiS AG. GS was involved in selecting the peptide antigens for the vaccines described in this manuscript and in vaccine design as well as in vaccine preparation. A patent protecting the antibodies mAb 9-3 and mAb 21-5 was filed (official patent number: PCT/EP2015/064701). AFFiRiS AG is a supporting member of the Christian Doppler Society. MZ and TMS received consultant honoraria from AFFiRiS AG. The authors confirm that the commercial affiliation of GS from AFFiRiS AG does not alter the authors' adherence to all PLOS ONE policies on sharing data and materials.
Figures




References
-
- Kintscher U, Hartge M, Hess K, Foryst-Ludwig A, Clemenz M, Wabitsch M, et al. (2008) T-lymphocyte infiltration in visceral adipose tissue: a primary event in adipose tissue inflammation and the development of obesity-mediated insulin resistance. Arterioscler Thromb Vasc Biol 28: 1304–1310. 10.1161/ATVBAHA.108.165100 - DOI - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Medical
Molecular Biology Databases
Research Materials
Miscellaneous

