The influence of stem cell source on transplant outcomes for pediatric patients with acute myeloid leukemia
- PMID: 30952678
- PMCID: PMC6457227
- DOI: 10.1182/bloodadvances.2018025908
The influence of stem cell source on transplant outcomes for pediatric patients with acute myeloid leukemia
Erratum in
-
Keating AK, Langenhorst J, Wagner JE, et al. The influence of stem cell source on transplant outcomes for pediatric patients with acute myeloid leukemia. Blood Adv. 2019;3(7):1118-1128.Blood Adv. 2020 Mar 24;4(6):1081. doi: 10.1182/bloodadvances.2020001753. Blood Adv. 2020. PMID: 32196555 Free PMC article. No abstract available.
Abstract
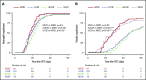
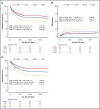
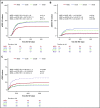
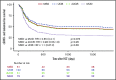
When hematopoietic stem cell transplant (HSCT) is necessary for children with acute myeloid leukemia (AML), there remains debate about the best stem cell source. Post-HSCT relapse is a common cause of mortality, and complications such as chronic graft versus host disease (cGVHD) are debilitating and life-threatening. To compare post-HSCT outcomes of different donor sources, we retrospectively analyzed consecutive transplants performed in several international centers from 2005 to 2015. A total of 317 patients were studied: 19% matched sibling donor (MSD), 23% matched unrelated donor (MUD), 39% umbilical cord blood (UCB), and 19% double UCB (dUCB) recipients. The median age at transplant was 10 years (range, 0.42-21 years), and median follow-up was 4.74 years (range, 4.02-5.39 years). Comparisons were made while controlling for patient, transplant, and disease characteristics. There were no differences in relapse, leukemia-free survival, or nonrelapse mortality. dUCB recipients had inferior survival compared with matched sibling recipients, but all other comparisons showed similar overall survival. Despite the majority of UCB transplants being HLA mismatched, the rates of cGVHD were low, especially compared with the well-matched MUD recipients (hazard ratio, 0.3; 95% confidence interval, 0.14-0.67; P = .02). The composite measure of cGVHD and leukemia-free survival (cGVHD-LFS), which represents both the quality of life and risk for mortality, was significantly better in the UCB compared with the MUD recipients (HR, 0.56; 95% confidence interval, 0.34-1; P = .03). In summary, the use of UCB is an excellent donor choice for pediatric patients with AML when a matched sibling cannot be identified.
© 2019 by The American Society of Hematology.
Conflict of interest statement
Conflict-of-interest disclosure: The authors declare no competing financial interests.
Figures


References
Publication types
MeSH terms
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Medical
Research Materials

