Heritability and genetic variance of dementia with Lewy bodies
- PMID: 30953760
- PMCID: PMC6588425
- DOI: 10.1016/j.nbd.2019.04.004
Heritability and genetic variance of dementia with Lewy bodies
Abstract
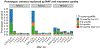
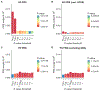
Recent large-scale genetic studies have allowed for the first glimpse of the effects of common genetic variability in dementia with Lewy bodies (DLB), identifying risk variants with appreciable effect sizes. However, it is currently well established that a substantial portion of the genetic heritable component of complex traits is not captured by genome-wide significant SNPs. To overcome this issue, we have estimated the proportion of phenotypic variance explained by genetic variability (SNP heritability) in DLB using a method that is unbiased by allele frequency or linkage disequilibrium properties of the underlying variants. This shows that the heritability of DLB is nearly twice as high as previous estimates based on common variants only (31% vs 59.9%). We also determine the amount of phenotypic variance in DLB that can be explained by recent polygenic risk scores from either Parkinson's disease (PD) or Alzheimer's disease (AD), and show that, despite being highly significant, they explain a low amount of variance. Additionally, to identify pleiotropic events that might improve our understanding of the disease, we performed genetic correlation analyses of DLB with over 200 diseases and biomedically relevant traits. Our data shows that DLB has a positive correlation with education phenotypes, which is opposite to what occurs in AD. Overall, our data suggests that novel genetic risk factors for DLB should be identified by larger GWAS and these are likely to be independent from known AD and PD risk variants.
Keywords: Dementia; Genetic correlation; Genetic variance; Lewy bodies.
Copyright © 2019 Elsevier Inc. All rights reserved.
Conflict of interest statement
Conflict of Interest Statement
Dr Shepherd and Halliday from Australia report no conflict of interests for this work.
Figures
References
-
- Aramillo Irizar P, Schäuble S, Esser D, Groth M, Frahm C, Priebe S, Baumgart M, Hartmann N, Marthandan S, Menzel U, Müller J, Schmidt S, Ast V, Caliebe A, König R, Krawczak M, Ristow M, Schuster S, Cellerino A, Diekmann S, Englert C, Hemmerich P, Sühnel J, Guthke R, Witte OW, Platzer M, Ruppin E, Kaleta C, 2018. Transcriptomic alterations during ageing reflect the shift from cancer to degenerative diseases in the elderly. Nat. Commun 9, 327. - PMC - PubMed
-
- Benyamin B, Pourcain B, Davis OS, Davies G, Hansell NK, Brion M-JA, Kirkpatrick RM, Cents RAM, Franic S, Miller MB, Haworth CMA, Meaburn E, Price TS, Evans DM, Timpson N, Kemp J, Ring S, McArdle W, Medland SE, Yang J, Harris SE, Liewald DC, Scheet P, Xiao X, Hudziak JJ, de Geus EJC, Wellcome Trust Case Control Consortium 2 (WTCCC2), Jaddoe VWV, Starr JM, Verhulst FC, Pennell C, Tiemeier H, Iacono WG, Palmer LJ, Montgomery GW, Martin NG, Boomsma DI, Posthuma D, McGue M, Wright MJ, Davey Smith G, Deary IJ, Plomin R, Visscher PM, 2014. Childhood intelligence is heritable, highly polygenic and associated with FNBP1L. Mol. Psychiatry 19, 253–258. - PMC - PubMed
-
- Bras J, Guerreiro R, Darwent L, Parkkinen L, Ansorge O, Escott-Price V, Hernandez DG, Nalls MA, Clark LN, Honig LS, Marder K, Van Der Flier WM, Lemstra A, Scheltens P, Rogaeva E, St George-Hyslop P, Londos E, Zetterberg H, Ortega Cubero S, Pastor P, Ferman TJ, Graff-Radford NR, Ross OA, Barber I, Braae A, Brown K, Morgan K, Maetzler W, Berg D, Troakes C, Al-Sarraj S, Lashley T, Compta Y, Revesz T, Lees A, Cairns N, Halliday GM, Mann D, Pickering-Brown S, Dickson DW, Singleton A, Hardy J, 2014. Genetic analysis implicates APOE, SNCA and suggests lysosomal dysfunction in the etiology of dementia with Lewy bodies. Hum. Mol. Genet 23, 6139–6146. - PMC - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Grants and funding
- MR/L501542/1/MRC_/Medical Research Council/United Kingdom
- P50 AG008702/AG/NIA NIH HHS/United States
- P50 NS053488/NS/NINDS NIH HHS/United States
- G0900652/MRC_/Medical Research Council/United Kingdom
- R01 AG033193/AG/NIA NIH HHS/United States
- R01 NS060113/NS/NINDS NIH HHS/United States
- MR/J004758/1/MRC_/Medical Research Council/United Kingdom
- P50 NS038377/NS/NINDS NIH HHS/United States
- G1001799/MRC_/Medical Research Council/United Kingdom
- P30 AG010124/AG/NIA NIH HHS/United States
- J-0804/PUK_/Parkinson's UK/United Kingdom
- R01 NS078086/NS/NINDS NIH HHS/United States
- U01 HG004446/HG/NHGRI NIH HHS/United States
- G1100540/MRC_/Medical Research Council/United Kingdom
- Z01 AG000949/ImNIH/Intramural NIH HHS/United States
- U01 NS100600/NS/NINDS NIH HHS/United States
- P50 AG005131/AG/NIA NIH HHS/United States
- U24 AG021886/AG/NIA NIH HHS/United States
- MR/K01417X/1/MRC_/Medical Research Council/United Kingdom
- P50 NS038370/NS/NINDS NIH HHS/United States
- P50 AG016574/AG/NIA NIH HHS/United States
- R01 CA141668/CA/NCI NIH HHS/United States
- P50 AG005146/AG/NIA NIH HHS/United States
- G0701075/MRC_/Medical Research Council/United Kingdom
- U01 AG032984/AG/NIA NIH HHS/United States
- Z01 ES101986/ImNIH/Intramural NIH HHS/United States
- G1001253/MRC_/Medical Research Council/United Kingdom
- P01 CA089392/CA/NCI NIH HHS/United States
- U01 AG016976/AG/NIA NIH HHS/United States
- G-1307/PUK_/Parkinson's UK/United Kingdom
- P01 AG003991/AG/NIA NIH HHS/United States
- P50 AG005681/AG/NIA NIH HHS/United States
- P01 AG014248/AG/NIA NIH HHS/United States
- P30 AG062429/AG/NIA NIH HHS/United States
- R01 HL105756/HL/NHLBI NIH HHS/United States
- P50 DA019706/DA/NIDA NIH HHS/United States
- ZIA AG000951/ImNIH/Intramural NIH HHS/United States
- HHSN268200782096C/HG/NHGRI NIH HHS/United States
- G0502157/MRC_/Medical Research Council/United Kingdom
- P50 CA084724/CA/NCI NIH HHS/United States
- G0400074/MRC_/Medical Research Council/United Kingdom
- P50 NS072187/NS/NINDS NIH HHS/United States
- R03 TW008019/TW/FIC NIH HHS/United States
- J-0901/PUK_/Parkinson's UK/United Kingdom
- P01 AG004953/AG/NIA NIH HHS/United States
- R01 NS037167/NS/NINDS NIH HHS/United States
- U54 NS110435/NS/NINDS NIH HHS/United States
- Z01 AG000951/ImNIH/Intramural NIH HHS/United States
- MR/L016397/1/MRC_/Medical Research Council/United Kingdom
- ZIA NS003154/ImNIH/Intramural NIH HHS/United States
- UL1 TR000040/TR/NCATS NIH HHS/United States
- WT_/Wellcome Trust/United Kingdom
- R01 AG048349/AG/NIA NIH HHS/United States
- MR/N026004/1/MRC_/Medical Research Council/United Kingdom
- MR/L023784/2/MRC_/Medical Research Council/United Kingdom
- MR/L010305/1/MRC_/Medical Research Council/United Kingdom
- MR/L022656/1/MRC_/Medical Research Council/United Kingdom
- G0901254/MRC_/Medical Research Council/United Kingdom
- P50 NS071674/NS/NINDS NIH HHS/United States
- U01 AG006786/AG/NIA NIH HHS/United States
- G0700943/MRC_/Medical Research Council/United Kingdom

