68Ga-FAPI PET/CT: Tracer Uptake in 28 Different Kinds of Cancer
- PMID: 30954939
- PMCID: PMC6581228
- DOI: 10.2967/jnumed.119.227967
68Ga-FAPI PET/CT: Tracer Uptake in 28 Different Kinds of Cancer
Abstract
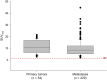
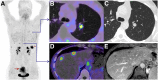
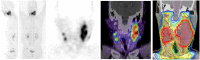
The recent development of quinoline-based PET tracers that act as fibroblast-activation-protein inhibitors (FAPIs) demonstrated promising preclinical and clinical results. FAP is overexpressed by cancer-associated fibroblasts of several tumor entities. Here, we quantify the tumor uptake on 68Ga-FAPI PET/CT of various primary and metastatic tumors to identify the most promising indications for future application. Methods:68Ga-FAPI PET/CT scans were requested by various referring physicians according to individual clinical indications that were considered insufficiently covered by 18F-FDG PET/CT or other imaging modalities. All PET/CT was performed 1 h after injection of 122-312 MBq of 68Ga-FAPI-04. We retrospectively identified 80 patients with histopathologically proven primary tumors or metastases or radiologically unequivocal metastatic lesions of histologically proven primary tumors. Tumor uptake was quantified by SUVmax and SUVmean (60% isocontour). Results: Eighty patients with 28 different tumor entities (54 primary tumors and 229 metastases) were evaluated. The highest average SUVmax (>12) was found in sarcoma, esophageal, breast, cholangiocarcinoma, and lung cancer. The lowest 68Ga-FAPI uptake (average SUVmax < 6) was observed in pheochromocytoma, renal cell, differentiated thyroid, adenoid cystic, and gastric cancer. The average SUVmax of hepatocellular, colorectal, head-neck, ovarian, pancreatic, and prostate cancer was intermediate (SUV 6-12). SUV varied across and within all tumor entities. Because of low background in muscle and blood pool (SUVmax < 2), the tumor-to-background contrast ratios were more than 3-fold in the intermediate and more than 6-fold in the high-intensity uptake group. Conclusion: Several highly prevalent cancers presented with remarkably high uptake and image contrast on 68Ga-FAPI PET/CT. The high and rather selective tumor uptake may open up new applications for noninvasive tumor characterization, staging examinations, or radioligand therapy.
Keywords: FAPI; PET/CT; breast cancer; colorectal cancer; lung cancer.
© 2019 by the Society of Nuclear Medicine and Molecular Imaging.
Figures


Comment in
-
68Ga FAPI PET/CT: Tracer Uptake in 28 Different Kinds of Cancer.Radiol Imaging Cancer. 2019 Sep 27;1(1):e194003. doi: 10.1148/rycan.2019194003. eCollection 2019 Sep. Radiol Imaging Cancer. 2019. PMID: 33778675 Free PMC article. No abstract available.
References
-
- Siveke JT. Fibroblast-activating protein: targeting the roots of the tumor microenvironment. J Nucl Med. 2018;59:1412–1414. - PubMed
-
- Hamson EJ, Keane FM, Tholen S, Schilling O, Gorrell MD. Understanding fibroblast activation protein (FAP): substrates, activities, expression and targeting for cancer therapy. Proteomics Clin Appl. 2014;8:454–463. - PubMed
-
- Lindner T, Loktev A, Altmann A, et al. Development of quinoline based theranostic ligands for the targeting of fibroblast activation protein. J Nucl Med. April 6, 2018. [Epub ahead of print]. - PubMed
MeSH terms
Substances
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Medical
Miscellaneous
