Current Controversy: Spikes, Bursts, and Synchrony in Generalized Absence Epilepsy: Unresolved Questions Regarding Thalamocortical Synchrony in Absence Epilepsy
- PMID: 30955423
- PMCID: PMC6610415
- DOI: 10.1177/1535759719835355
Current Controversy: Spikes, Bursts, and Synchrony in Generalized Absence Epilepsy: Unresolved Questions Regarding Thalamocortical Synchrony in Absence Epilepsy
Abstract
Absence epilepsy is a disorder of thalamocortical networks. Animal models have provided detailed information regarding the core cellular, synaptic, and network features that contribute to the electroencephalogram spike and wave discharge characteristic of typical absence epilepsy. Understanding of seizure networks and dynamics is a critical step toward improving treatments, yet competing conceptual models have evolved to explain seizure initiation and propagation. Recent studies have questioned 2 key model concepts: (1) T-type Ca2+ channel-dependent burst firing in thalamic relay neurons may not be essential for seizure generation, bringing into question the proposed mechanism for the antiepileptic drug ethosuximide in reducing thalamic bursting and (2) widespread synchronized neural activity may not be a core feature of the seizures, indicating that reductions in synchrony would not be a productive therapeutic goal. In this review, I will discuss these current findings, highlight the innovative approaches that have enabled these insights, and provide a unified framework that incorporates these sometimes-conflicting ideas. Finally, I lay out future work that will be necessary to finally resolve the remaining issues.
Conflict of interest statement
Figures

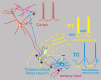
References
-
- Hunter J, Jasper H. Reactions of unanaesthetised animals to thalamic stimulation. Trans Am Neurol Assoc. 1948;73(73 Annual Meet):171. - PubMed
-
- Gloor P, Avoli M, Kostopoulos G. Thalamo-cortical relationships in generalized epilepsy with bilaterally synchronous spike-and-wave discharge In Generalized Epilepsy: Neurobiological Approaches, Boston, MA: Birkhäuser; 1990;190–212.
-
- Maheshwari A, Noebels JL. Monogenic models of absence epilepsy: windows into the complex balance between inhibition and excitation in thalamocortical microcircuits. Prog Brain Res. 2014;213:223–252. - PubMed
-
- McCormick DA, Contreras D. On the cellular and network bases of epileptic seizures. Annu Rev Physiol. 2001;63:815–846. - PubMed
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Miscellaneous

