Insulin Receptor Associates with Promoters Genome-wide and Regulates Gene Expression
- PMID: 30955890
- PMCID: PMC6478446
- DOI: 10.1016/j.cell.2019.02.030
Insulin Receptor Associates with Promoters Genome-wide and Regulates Gene Expression
Abstract
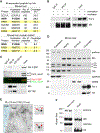
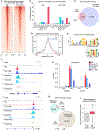
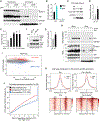
Insulin receptor (IR) signaling is central to normal metabolic control and dysregulated in prevalent chronic diseases. IR binds insulin at the cell surface and transduces rapid signaling via cytoplasmic kinases. However, mechanisms mediating long-term effects of insulin remain unclear. Here, we show that IR associates with RNA polymerase II in the nucleus, with striking enrichment at promoters genome-wide. The target genes were highly enriched for insulin-related functions including lipid metabolism and protein synthesis and diseases including diabetes, neurodegeneration, and cancer. IR chromatin binding was increased by insulin and impaired in an insulin-resistant disease model. Promoter binding by IR was mediated by coregulator host cell factor-1 (HCF-1) and transcription factors, revealing an HCF-1-dependent pathway for gene regulation by insulin. These results show that IR interacts with transcriptional machinery at promoters and identify a pathway regulating genes linked to insulin's effects in physiology and disease.
Keywords: HCFC1; INSR; RNA polymerase II; coregulator host cell factor-1; gene promoter; insulin receptor signaling; nuclear receptor tyrosine kinase; transcription factor.
Copyright © 2019 Elsevier Inc. All rights reserved.
Conflict of interest statement
Declaration of Interests
The authors declare no competing interests.
Figures




Comment in
-
Insulin and the insulin receptor regulate gene expression.Nat Rev Endocrinol. 2019 Jun;15(6):315. doi: 10.1038/s41574-019-0206-6. Nat Rev Endocrinol. 2019. PMID: 30976117 No abstract available.
-
The insulin receptor goes nuclear.Cell Res. 2019 Jul;29(7):509-511. doi: 10.1038/s41422-019-0185-0. Cell Res. 2019. PMID: 31160720 Free PMC article. No abstract available.
References
-
- Babu M, Gagarinova A, and Emili A (2011). Array-based synthetic genetic screens to map bacterial pathways and functional networks in Escherichia coli. Methods Mol Biol 781, 99–126. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Molecular Biology Databases
Research Materials
Miscellaneous

