Somatic Mutations Increase Hepatic Clonal Fitness and Regeneration in Chronic Liver Disease
- PMID: 30955891
- PMCID: PMC6519461
- DOI: 10.1016/j.cell.2019.03.026
Somatic Mutations Increase Hepatic Clonal Fitness and Regeneration in Chronic Liver Disease
Abstract
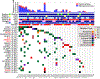
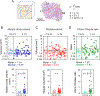
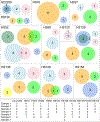
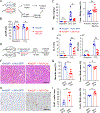
Normal tissues accumulate genetic changes with age, but it is unknown if somatic mutations promote clonal expansion of non-malignant cells in the setting of chronic degenerative diseases. Exome sequencing of diseased liver samples from 82 patients revealed a complex mutational landscape in cirrhosis. Additional ultra-deep sequencing identified recurrent mutations in PKD1, PPARGC1B, KMT2D, and ARID1A. The number and size of mutant clones increased as a function of fibrosis stage and tissue damage. To interrogate the functional impact of mutated genes, a pooled in vivo CRISPR screening approach was established. In agreement with sequencing results, examination of 147 genes again revealed that loss of Pkd1, Kmt2d, and Arid1a promoted clonal expansion. Conditional heterozygous deletion of these genes in mice was also hepatoprotective in injury assays. Pre-malignant somatic alterations are often viewed through the lens of cancer, but we show that mutations can promote regeneration, likely independent of carcinogenesis.
Copyright © 2019 Elsevier Inc. All rights reserved.
Conflict of interest statement
Declaration of Interests
The authors declare no competing interests.
Figures


Comment in
-
Mutational landscape in liver disease - fit for regeneration?Nat Rev Gastroenterol Hepatol. 2019 Jun;16(6):326-327. doi: 10.1038/s41575-019-0151-9. Nat Rev Gastroenterol Hepatol. 2019. PMID: 31019267 No abstract available.
-
Beneficial Noncancerous Mutations in Liver Disease.Trends Genet. 2019 Jul;35(7):475-477. doi: 10.1016/j.tig.2019.05.002. Epub 2019 May 28. Trends Genet. 2019. PMID: 31151757
-
Somatic Mutations in Liver Disease: Adaptation Without Carcinogenesis?Hepatology. 2020 Jun;71(6):2162-2163. doi: 10.1002/hep.31169. Hepatology. 2020. PMID: 32034958 No abstract available.
References
-
- Aihara T, Noguchi S, Sasaki Y, Nakano H, and Imaoka S (1994). Clonal analysis of regenerative nodules in hepatitis C virus-induced liver cirrhosis. Gastroenterology 107, 1805–1811. - PubMed
-
- Chen X, Schulz-Trieglaff O, Shaw R, Barnes B, Schlesinger F, Kallberg M, Cox AJ, Kruglyak S, and Saunders CT (2016). Manta: rapid detection of structural variants and indels for germline and cancer sequencing applications. Bioinformatics 32, 1220–1222. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Medical
Molecular Biology Databases
Miscellaneous

