Safety and immunogenicity of an 8 year interval heterologous prime-boost influenza A/H7N7-H7N9 vaccination
- PMID: 30955980
- PMCID: PMC6519114
- DOI: 10.1016/j.vaccine.2019.03.071
Safety and immunogenicity of an 8 year interval heterologous prime-boost influenza A/H7N7-H7N9 vaccination
Abstract
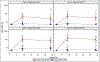
Background: Influenza A/H7N9 viruses are undergoing antigenic drift since their emergence in 2013, and vaccination strategies are needed for pandemic preparedness. Two doses of adjuvanted monovalent inactivated influenza A/H7N9 vaccine (IIV1 A/H7N9) are needed for optimal serological responses. However, administering 2 doses in a pandemic setting might be challenging. We evaluated the immunogenicity of "boosting" with IIV1 A/H7N9 in subjects "primed" 8 years previously with IIV1 A/H7N7.
Methods: We administered 1 booster dose containing 45 mcg of IIV1 A/H7N9 hemagglutinin to 17 recipients of 2 prior doses of IIV1 A/H7N7, and to 10 influenza A/H7-naïve subjects. We tested their post-boosting sera for antibodies (Ab) against homologous influenza A/H7N9 using a hemagglutination inhibition assay; and compared their Ab titers to those in stored sera from recipients of AS03-adjuvanted IIV1 A/H7N9 against 9 strains of influenza A/H7N9 viruses.
Results: The percentage of subjects with Ab titers ≥40 on Days 9 and 29 post boosting, respectively, was 65% and 41% in primed subjects and 10% and 0% in unprimed subjects. The Ab titers in recipients of AS03-adjuvanted IIV1 A/H7N9 were higher than those in the prime-boost group against a panel of influenza A/H7N9 viruses, except for 2 highly pathogenic strains.
Conclusions: Priming with IIV1 A/H7 results in serological responses following a delayed boost with 1 dose of unadjuvanted IIV1 A/H7N9, despite lack of antibody response after the prime. Optimizing prime-boost approaches would benefit pandemic preparedness. ClinicalTrials.gov identifier: NCT02586792.
Keywords: Avian; Influenza; Influenza A/H7N9; Pandemic; Prime-boost; Vaccines.
Copyright © 2019 Elsevier Ltd. All rights reserved.
Conflict of interest statement
The authors report no conflicts of interest pertaining to the conduct and reporting of this clinical trial
Declaration of interests
The authors declare that they have no known competing financial interests or personal relationships that could have appeared to influence the work reported in this paper.
Figures




References
-
- Su S, Gu M, Liu D, Cui J, Gao GF, Zhou J, et al. Epidemiology, Evolution, and Pathogenesis of H7N9 Influenza Viruses in Five Epidemic Waves since 2013 in China. Trends Microbiol. 2017;25:713–28. - PubMed
-
- Ding X, Luo J, Quan L, Wu A, Jiang T. Evolutionary genotypes of influenza A (H7N9) viruses over five epidemic waves in China. Infect Genet Evol. 2017;55:269–76. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Associated data
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Medical

