A Combined Approach Reveals a Regulatory Mechanism Coupling Src's Kinase Activity, Localization, and Phosphotransferase-Independent Functions
- PMID: 30956043
- PMCID: PMC6474823
- DOI: 10.1016/j.molcel.2019.02.003
A Combined Approach Reveals a Regulatory Mechanism Coupling Src's Kinase Activity, Localization, and Phosphotransferase-Independent Functions
Abstract
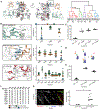
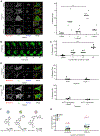
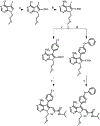
Multiple layers of regulation modulate the activity and localization of protein kinases. However, many details of kinase regulation remain incompletely understood. Here, we apply saturation mutagenesis and a chemical genetic method for allosterically modulating kinase global conformation to Src kinase, providing insight into known regulatory mechanisms and revealing a previously undiscovered interaction between Src's SH4 and catalytic domains. Abrogation of this interaction increased phosphotransferase activity, promoted membrane association, and provoked phosphotransferase-independent alterations in cell morphology. Thus, Src's SH4 domain serves as an intramolecular regulator coupling catalytic activity, global conformation, and localization, as well as mediating a phosphotransferase-independent function. Sequence conservation suggests that the SH4 domain regulatory interaction exists in other Src-family kinases. Our combined approach's ability to reveal a regulatory mechanism in one of the best-studied kinases suggests that it could be applied broadly to provide insight into kinase structure, regulation, and function.
Keywords: Src; activity; allostery; kinase; regulation.
Copyright © 2019 Elsevier Inc. All rights reserved.
Figures


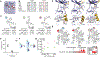


References
-
- Bjorge JD, Bellagamba C, Cheng H-C, Tanaka A, Wang JH, and Fujita DJ (1995). Characterization of Two Activated Mutants of Human pp60c-srcThat Escape c-Src Kinase Regulation by Distinct Mechanisms. Journal of Biological Chemistry 270, 24222–24228. - PubMed
-
- Boggon TJ, and Eck MJ (2004). Structure and regulation of Src family kinases. Oncogene 23, 7918–7927. - PubMed
-
- Charras GT (2008). A short history of blebbing. J Microsc 231, 466–478. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Molecular Biology Databases
Research Materials
Miscellaneous

