Effects of Local Ischemic Compression on Upper Limb Latent Myofascial Trigger Points: A Study of Subjective Pain and Linear Motor Performance
- PMID: 30956821
- PMCID: PMC6425406
- DOI: 10.1155/2019/5360924
Effects of Local Ischemic Compression on Upper Limb Latent Myofascial Trigger Points: A Study of Subjective Pain and Linear Motor Performance
Abstract
Objective: To analyse the effect of the manual ischemic compression (IC) on the upper limb motor performance (MP) in patients with LTrPs.
Materials and methods: A quasiexperimental study was performed in twenty subjects allocated to either patients group with LTrPs (PG, n=10) or healthy group with no symptoms (HG, n=10). Subjective pain and linear MP (movement time and Fitts' Law) were assessed before and after a linear tapping task. Data were analysed with mixed factorial ANOVA for intergroup linear motor performance differences and dependent t-student test for intragroup pain differences.
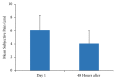
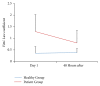
Results: PG had a linear MP lower than the HG before treatment (p < 0.05). After IC, the PG showed a significant decrease of pain (4.07 ± 1.91 p < 0.001). Furthermore, the movement time (15.70 ± 2.05 p < 0.001) and the Fitts' Law coefficient (0.80 ± 0.53 p < 0.001) were significantly reduced. However, one IC session did not allow the PG to get the same MP than the HG (p < 0.05).
Conclusion: The results suggest the IC effectiveness on pain and MP impairment in subjects with LTrPs. However, the MP of these patients is only partially improved after the IC application.
Figures

Similar articles
-
Relationship between Alexithymia and latent trigger points in the upper Trapezius.Biopsychosoc Med. 2017 Dec 11;11:31. doi: 10.1186/s13030-017-0116-6. eCollection 2017. Biopsychosoc Med. 2017. PMID: 29238400 Free PMC article.
-
Children with congenital spastic hemiplegia obey Fitts' Law in a visually guided tapping task.Exp Brain Res. 2007 Mar;177(4):431-9. doi: 10.1007/s00221-006-0698-x. Epub 2006 Sep 22. Exp Brain Res. 2007. PMID: 17019607
-
Prevalence of myofascial trigger points and diagnostic criteria of different muscles in function of the medial longitudinal arch.Arch Phys Med Rehabil. 2015 Jun;96(6):1123-30. doi: 10.1016/j.apmr.2015.02.017. Epub 2015 Mar 3. Arch Phys Med Rehabil. 2015. PMID: 25748145
-
Changes in a patient with neck pain after application of ischemic compression as a trigger point therapy.J Back Musculoskelet Rehabil. 2010;23(2):101-4. doi: 10.3233/BMR-2010-0255. J Back Musculoskelet Rehabil. 2010. PMID: 20555123
-
Clinical implication of latent myofascial trigger point.Curr Pain Headache Rep. 2013 Aug;17(8):353. doi: 10.1007/s11916-013-0353-8. Curr Pain Headache Rep. 2013. PMID: 23801006 Review.
Cited by
-
Pressing Intervention Promotes the Skeletal Muscle Repair of Traumatic Myofascial Trigger Points in Rats.J Pain Res. 2021 Oct 15;14:3267-3278. doi: 10.2147/JPR.S333705. eCollection 2021. J Pain Res. 2021. PMID: 34703302 Free PMC article.
References
-
- Travell J. G., Simons D. G. The Trigger Point Manual: The Lower Extremities. 1st. Vol. 2. Baltimore, Maryland, Mo, USA: Williams & Wilkins; 1992. Myofascial pain and dysfunction.
-
- Huguenin L. K. Myofascial trigger points: the current evidence. Physical Therapy in Sport. 2004;5(1):2–12. doi: 10.1016/j.ptsp.2003.11.002. - DOI
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources

