Efficacy of chemical sanitizers against Bacillus cereus on food contact surfaces with scratch and biofilm
- PMID: 30956871
- PMCID: PMC6431354
- DOI: 10.1007/s10068-018-0482-2
Efficacy of chemical sanitizers against Bacillus cereus on food contact surfaces with scratch and biofilm
Abstract
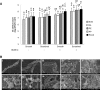
This study was performed to investigate the efficacy of chemical sanitizers (viz., chlorine, chlorine dioxide, alcohol, and quaternary ammonium compound) against Bacillus cereus on five food contact materials under different conditions (smooth vs. scratched and with vs. without biofilms). After incubating materials in B. cereus suspension, cell adhesion on a smooth surface (10 cm2) was in the following ascending order: stainless steel (7.36 ± 0.08 log CFU), glass (7.51 ± 0.26 log CFU), polyethylene (7.66 ± 0.30 log CFU), polypropylene (7.76 ± 0.30 log CFU), and wood (8.02 ± 0.33 log CFU). The efficacy of sanitizers was dramatically reduced in the presence of a biofilm on all materials. Among four different chemical sanitizers, chlorine showed the best bactericidal activity against B. cereus on the surface with scratch and biofilm. Selection of adequate materials, maintenance of a smooth surface, and inhibition of biofilm formation are good practices for food safety.
Keywords: Bacillus cereus; Biofilm; Food contact surface; Sanitizing efficacy; Scratched surface.
Figures
References
-
- Adetunji VO, Isola TO. Crystal violet binding assay for assessment of biofilm formation by Listeria monocytogenes and Listeria spp on wood, steel and glass surfaces. Glob Vet. 2011;6(1):6–10.
-
- Araújo EA, Bernardes PC, Andrade NJ, Fernandes PE, Sá JPN. Gibbs free energy of adhesion of Bacillus cereus isolated from dairy plants on different food processing surfaces evaluated by the hydrophobicity. Int J Food Sci Technol. 2009;44:2519–2525. doi: 10.1111/j.1365-2621.2009.02078.x. - DOI
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
