Reduction of total, organic, and inorganic arsenic content in Hizikia fusiforme (Hijiki)
- PMID: 30956875
- PMCID: PMC6431341
- DOI: 10.1007/s10068-018-0501-3
Reduction of total, organic, and inorganic arsenic content in Hizikia fusiforme (Hijiki)
Abstract
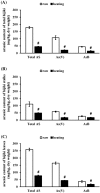
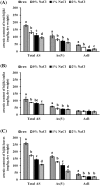
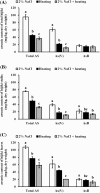
This study aimed to evaluate the reduction of total, organic, and inorganic arsenic content in Hizikia fusiforme (hijiki). Initially, the six most common arsenic compounds in hijiki and its organs were evaluated, among which only arsenate and arsenobetaine were detected. Thereafter, the entire plant, including the stalk and leaves, was treated with heat and NaCl solution, individually and in combination. Heating at 90 °C for 5 min significantly reduced arsenic content in hijiki by approximately 33-80%. Treatment with NaCl solution significantly reduced arsenic content in hijiki, except for arsenobetaine content in the stalk. Combinatorial treatment further decreased arsenic content by more than 5-20%. In conclusion, consumption of hijiki after boiling at 90 °C and soaking in 2% NaCl solution reduces the intake of inorganic arsenic by consumers.
Keywords: Heating; Inorganic arsenic; Organic arsenic; Soaking; Total arsenic.
Conflict of interest statement
Compliance with ethical standardsThe authors declare that they have no conflict of interest.
Figures
References
-
- Abernathy CO. Bioaccumulation of arsenic (As) in fish & toxicity of as species. Washington DC, USA: US Environmental Protection Agency; 2003.
-
- Agency for Toxic Substances and Disease Registry. Public health statement for arsenic. Available from: https://www.atsdr.cdc.gov/spl/resources/index.html. Accessed June 27, 2018
-
- Baek HI, Kim SW, Ha KC, Kim HM, So BO, Choi EK, Park EO, Jeon BJ, Park BH, Nam TJ, Kim IH, Chae SW. Effectiveness of Hizikia fusiformis extract on erosive gastritis: A4-week, randomized, double-blind and placebo-controlled trial. Int. J. Pharmacol. 2015;11(1):719–725.
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
