Newborn Screening for Lysosomal Storage Disorders: Methodologies for Measurement of Enzymatic Activities in Dried Blood Spots
- PMID: 30957052
- PMCID: PMC6448570
- DOI: 10.3390/ijns5010001
Newborn Screening for Lysosomal Storage Disorders: Methodologies for Measurement of Enzymatic Activities in Dried Blood Spots
Abstract
All worldwide newborn screening (NBS) for lysosomal storage diseases (LSDs) is performed as a first-tier test by measurement of lysosomal enzymatic activities in dried blood spots (DBS). The currently two available methodologies used for measurement of enzymatic activities are tandem mass spectrometry (MS/MS) and digital microfluidics fluorimetry (DMF-F). In this chapter we summarize the workflows for the two platforms. Neither platform is fully automated, but the relative ease of workflow will be dependent upon the specific operation of each newborn screening laboratory on a case-by-case basis. We provide the screen positive rate (the number of below cutoff newborns per 100,000 newborns) from all NBS laboratories worldwide carrying out MS/MS-based NBS of one or more LSDs. The analytical precision of the MS/MS method is higher than that for DMF-F as shown by analysis of a common set of quality control DBS by the Centers for Disease Control and Prevention (CDC). Both the MS/MS and DMF-F platforms enable multiplexing of the LSD enzymes. An advantage of MS/MS over DMF-F is the ability to include assays of enzymatic activities and biomarkers for which no fluorimetric methods exist. Advantages of DMF-F over MS/MS are: 1) Simple to use technology with same-day turn-around time for the lysosomal enzymes with the fastest rates compared to MS/MS requiring overnight analytical runs.; 2) The DMF-F instrumentation, because of its simplicity, requires less maintenance than the MS/MS platform.
Keywords: cutoff values; diagnosis; dried blood spots; enzymatic activity assays; lysosomal storage diseases; newborn screening; tandem mass spectrometry.
Conflict of interest statement
Gelb is a consultant for PerkinElmer and has received research funding from Biomarin, Shire, and Ultrageneyx corporations. Lukacs received travel and research grants and honoraria from Sanofi Genzyme B.V., Netherlands, BioMarin Ltd, Dublin, Ireland, Alexion Pharma GmbH, Munich, Germany, Ultragenyx, Zurich, Switzerland, PerkinElmer Life Science, Turku, Finland.
Figures
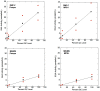
References
-
- Sista R.S., Eckhardt A.E., Wang T., Graham C., Rouse J.L., Norton S.M., Srinivasan V., Pollack M.G., Tolun A.A., Bali D., et al. Digital microfluidic platform for multiplexing enzyme assays, implications for lysosomal storage disease screening in newborns. Clin. Chem. 2011;57:1444–1451. doi: 10.1373/clinchem.2011.163139. - DOI - PMC - PubMed
-
- Elliott S., Buroker N., Cournoyer J.J., Potier A.M., Trometer J.D., Elbin C., Schermer M.J., Kantola J., Boyce A., Turecek F., et al. Pilot study of newborn screening for six lysosomal storage diseases using Tandem Mass Spectrometry. Mol. Genet. Metab. 2016;118:304–309. doi: 10.1016/j.ymgme.2016.05.015. - DOI - PMC - PubMed
-
- Liu Y., Yi F., Kumar A.B., Kumar Chennamaneni N., Hong X., Scott C.R., Gelb M.H., Turecek F. Multiplex Tandem Mass Spectrometry Enzymatic Activity Assay for Newborn Screening of the Mucopolysaccharidoses and Type 2 Neuronal Ceroid Lipofuscinosis. Clin. Chem. 2017;63:1118–1126. doi: 10.1373/clinchem.2016.269167. - DOI - PMC - PubMed
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Research Materials
Miscellaneous

