Current knowledge on enzymatic PET degradation and its possible application to waste stream management and other fields
- PMID: 30957199
- PMCID: PMC6505623
- DOI: 10.1007/s00253-019-09717-y
Current knowledge on enzymatic PET degradation and its possible application to waste stream management and other fields
Abstract
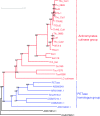
Enzymatic hydrolysis of polyethylene terephthalate (PET) has been the subject of extensive previous research that can be grouped into two categories, viz. enzymatic surface modification of polyester fibers and management of PET waste by enzymatic hydrolysis. Different enzymes with rather specific properties are required for these two processes. Enzymatic surface modification is possible with several hydrolases, such as lipases, carboxylesterases, cutinases, and proteases. These enzymes should be designated as PET surface-modifying enzymes and should not degrade the building blocks of PET but should hydrolyze the surface polymer chain so that the intensity of PET is not weakened. Conversely, management of PET waste requires substantial degradation of the building blocks of PET; therefore, only a limited number of cutinases have been recognized as PET hydrolases since the first PET hydrolase was discovered by Müller et al. (Macromol Rapid Commun 26:1400-1405, 2005). Here, we introduce current knowledge on enzymatic degradation of PET with a focus on the key class of enzymes, PET hydrolases, pertaining to the definition of enzymatic requirements for PET hydrolysis, structural analyses of PET hydrolases, and the reaction mechanisms. This review gives a deep insight into the structural basis and dynamics of PET hydrolases based on the recent progress in X-ray crystallography. Based on the knowledge accumulated to date, we discuss the potential for PET hydrolysis applications, such as in designing waste stream management.
Keywords: Catalytic mechanism; Cutinase; PET hydrolase; PETase; Potential application; Structural analyses.
Conflict of interest statement
Conflict of interest
The authors declare that they have no conflicts of interests.
Ethical statement
This work does not contain any studies with human participants or animals performed by any of the authors.
Figures

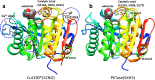
References
-
- Austin HP, Allen MD, Donohoe BS, Rorrer NA, Kearns FL, Silveira RL, Pollard BC, Dominick G, Duman R, Omari KE, Mykhaylyk V, Wagner A, Michener WE, Amore A, Skaf MS, Crowley MF, Thorne AW, Johnson CW, Woodcock HL, McGeehan JE, Beckham GT. Characterization and engineering of a plastic-degrading aromatic polyesterase. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 2018;115:E4350–E4357. doi: 10.1073/pnas.1718804115. - DOI - PMC - PubMed
-
- Barth M, Oeser T, Wei R, Then J, Schmidt J, Zimmermann W. Effect of hydrolysis products on the enzymatic degradation of polyethylene terephthalate nanoparticles by a polyester hydrolase from Thermobifida fusca. Biochem Eng J. 2015;93:222–228. doi: 10.1016/j.bej.2014.10.012. - DOI
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Molecular Biology Databases

