Parkinson's disease age at onset genome-wide association study: Defining heritability, genetic loci, and α-synuclein mechanisms
- PMID: 30957308
- PMCID: PMC6579628
- DOI: 10.1002/mds.27659
Parkinson's disease age at onset genome-wide association study: Defining heritability, genetic loci, and α-synuclein mechanisms
Abstract
Background: Increasing evidence supports an extensive and complex genetic contribution to PD. Previous genome-wide association studies (GWAS) have shed light on the genetic basis of risk for this disease. However, the genetic determinants of PD age at onset are largely unknown.
Objectives: To identify the genetic determinants of PD age at onset.
Methods: Using genetic data of 28,568 PD cases, we performed a genome-wide association study based on PD age at onset.
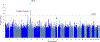
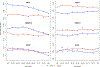
Results: We estimated that the heritability of PD age at onset attributed to common genetic variation was ∼0.11, lower than the overall heritability of risk for PD (∼0.27), likely, in part, because of the subjective nature of this measure. We found two genome-wide significant association signals, one at SNCA and the other a protein-coding variant in TMEM175, both of which are known PD risk loci and a Bonferroni-corrected significant effect at other known PD risk loci, GBA, INPP5F/BAG3, FAM47E/SCARB2, and MCCC1. Notably, SNCA, TMEM175, SCARB2, BAG3, and GBA have all been shown to be implicated in α-synuclein aggregation pathways. Remarkably, other well-established PD risk loci, such as GCH1 and MAPT, did not show a significant effect on age at onset of PD.
Conclusions: Overall, we have performed the largest age at onset of PD genome-wide association studies to date, and our results show that not all PD risk loci influence age at onset with significant differences between risk alleles for age at onset. This provides a compelling picture, both within the context of functional characterization of disease-linked genetic variability and in defining differences between risk alleles for age at onset, or frank risk for disease. © 2019 International Parkinson and Movement Disorder Society.
Keywords: GBA; Parkinson's disease; SNCA; TMEM175; age at onset.
© 2019 International Parkinson and Movement Disorder Society.
Figures
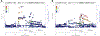
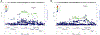

References
-
- Dorsey ER, Bloem BR. The Parkinson Pandemic-A Call to Action. JAMA Neurol 2018;75(1):9–10. - PubMed
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
- Z01 AG000949/ImNIH/Intramural NIH HHS/United States
- R01 CA141668/CA/NCI NIH HHS/United States
- G0701075/MRC_/Medical Research Council/United Kingdom
- G1100643/MRC_/Medical Research Council/United Kingdom
- Z01 ES101986/ImNIH/Intramural NIH HHS/United States
- R01 NS037167/NS/NINDS NIH HHS/United States
- MR/N026004/1/MRC_/Medical Research Council/United Kingdom
- J-1101/PUK_/Parkinson's UK/United Kingdom
- G0700943/MRC_/Medical Research Council/United Kingdom
- G1001799/MRC_/Medical Research Council/United Kingdom
- J-0804/PUK_/Parkinson's UK/United Kingdom
- Z01 AG000932/ImNIH/Intramural NIH HHS/United States
- MR/L501542/1/MRC_/Medical Research Council/United Kingdom
- MR/K01417X/1/MRC_/Medical Research Council/United Kingdom
- G-0907/PUK_/Parkinson's UK/United Kingdom
- ZIA NS003154/ImNIH/Intramural NIH HHS/United States
- WT_/Wellcome Trust/United Kingdom
- G0901254/MRC_/Medical Research Council/United Kingdom
- P50 NS071674/NS/NINDS NIH HHS/United States
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Medical
Miscellaneous

