Recurrent Stroke With Rivaroxaban Compared With Aspirin According to Predictors of Atrial Fibrillation: Secondary Analysis of the NAVIGATE ESUS Randomized Clinical Trial
- PMID: 30958508
- PMCID: PMC6583060
- DOI: 10.1001/jamaneurol.2019.0617
Recurrent Stroke With Rivaroxaban Compared With Aspirin According to Predictors of Atrial Fibrillation: Secondary Analysis of the NAVIGATE ESUS Randomized Clinical Trial
Abstract
Importance: The NAVIGATE ESUS randomized clinical trial found that 15 mg of rivaroxaban per day does not reduce stroke compared with aspirin in patients with embolic stroke of undetermined source (ESUS); however, it substantially reduces stroke risk in patients with atrial fibrillation (AF).
Objective: To analyze whether rivaroxaban is associated with a reduction of recurrent stroke among patients with ESUS who have an increased risk of AF.
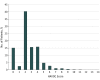
Design, setting, and participants: Participants were stratified by predictors of AF, including left atrial diameter, frequency of premature atrial contractions, and HAVOC score, a validated scheme using clinical features. Treatment interactions with these predictors were assessed. Participants were enrolled between December 2014 and September 2017, and analysis began March 2018.
Intervention: Rivaroxaban treatment vs aspirin.
Main outcomes and measures: Risk of ischemic stroke.
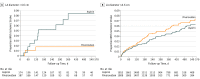
Results: Among 7112 patients with a mean (SD) age of 67 (9.8) years, the mean (SD) HAVOC score was 2.6 (1.8), the mean (SD) left atrial diameter was 3.8 (1.4) cm (n = 4022), and the median (interquartile range) daily frequency of premature atrial contractions was 48 (13-222). Detection of AF during follow-up increased for each tertile of HAVOC score: 2.3% (score, 0-2), 3.0% (score, 3), and 5.8% (score, >3); however, neither tertiles of the HAVOC score nor premature atrial contractions frequency impacted the association of rivaroxaban with recurrent ischemic stroke (P for interaction = .67 and .96, respectively). Atrial fibrillation annual incidence increased for each tertile of left atrial diameter (2.0%, 3.6%, and 5.2%) and for each tertile of premature atrial contractions frequency (1.3%, 2.9%, and 7.0%). Among the predefined subgroup of patients with a left atrial diameter of more than 4.6 cm (9% of overall population), the risk of ischemic stroke was lower among the rivaroxaban group (1.7% per year) compared with the aspirin group (6.5% per year) (hazard ratio, 0.26; 95% CI, 0.07-0.94; P for interaction = .02).
Conclusions and relevance: The HAVOC score, left atrial diameter, and premature atrial contraction frequency predicted subsequent clinical AF. Rivaroxaban was associated with a reduced risk of recurrent stroke among patients with ESUS and moderate or severe left atrial enlargement; however, this needs to be independently confirmed before influencing clinical practice.
Conflict of interest statement
Figures
Comment in
-
Left Atrial Enlargement Could Be Detected on Extended Computed Tomography Angiography Within Initial Stroke Assessment.JAMA Neurol. 2020 Jan 1;77(1):134. doi: 10.1001/jamaneurol.2019.3791. JAMA Neurol. 2020. PMID: 31710333 No abstract available.
-
Left Atrial Enlargement Could Be Detected on Extended Computed Tomography Angiography Within Initial Stroke Assessment-Reply.JAMA Neurol. 2020 Jan 1;77(1):134-135. doi: 10.1001/jamaneurol.2019.3794. JAMA Neurol. 2020. PMID: 31710343 No abstract available.