Activation of cGMP/PKG/p65 signaling associated with PDE5-Is downregulates CCL5 secretion by CD8 + T cells in benign prostatic hyperplasia
- PMID: 30958912
- PMCID: PMC6593656
- DOI: 10.1002/pros.23801
Activation of cGMP/PKG/p65 signaling associated with PDE5-Is downregulates CCL5 secretion by CD8 + T cells in benign prostatic hyperplasia
Abstract
Background: Benign prostatic hyperplasia (BPH) is the most common urological disease in elderly men, but the underlying pathophysiological mechanisms are complex and not fully understood. Phosphodiesterase type 5 inhibitors (PDE5-Is) used to treat BPH could upregulate the cyclic guanosine monophosphate (cGMP)-dependent protein kinase G (PKG) signaling, which was shown to blunt inflammation in the prostate. Our previous findings indicate that CD8+ T cells promote the proliferation of BPH epithelial cells (BECs) in low androgen conditions through secretion of CCL5; however, the role of the cGMP/PKG pathway in the process is unclear.
Methods: Paraffin-embedded tissues were used for expression quantity of CD8+ T cells, CCL5, cyclin D1, and PDE5 protein by immunohistology in prostate specimens which were/were not treated with finasteride 5 mg daily for at least 6 months before surgery. BPH-1 cells were cocultured with or without CD8 + T cells or PDE5-Is in low androgen conditions for 4 days. The conditioned media, BPH-1 cells, and CD8 + T cells were harvested for the subsequent experiments. The quantitative polymerase chain reaction was used for assaying the level of messenger RNA expression of CCL5. CCL5 in the conditioned media was detected by the enzyme-linked immunosorbent assay. The effect of PDE5-Is on cocultured BPH-1/CD8 + T-cell proliferation was detected by the cell counting kit-8. A high-fat diet (HFD)-induced prostatic hyperplasia rat model was used to investigate the effect of cGMP/PKG activation in CD8 + T cells in vivo.
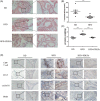
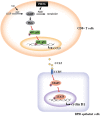
Results: CD8+ T-cell infiltration into human BPH tissues was positively correlated with the expression of CCL5, cyclin D1, and PDE5, whereas in an HFD-induced prostatic hyperplasia rat model, the activation of the cGMP/PKG signaling by a PDE5-I could suppress the CD8 + T-cell infiltration and the CCL5 and cyclin D1 expression. Furthermore, the activation of the cGMP/PKG pathway inhibited CCL5 secretion by CD8 + T cells by downregulating nuclear factor-κB p65 phosphorylation, which reduced the growth of BPH-1 through CCL5/STAT5/CCND1 signaling.
Conclusions: Our results indicate that the upregulation of the cGMP/PKG/p65 signaling reduces CCL5 secretion in CD8 + T cells, which in turn decreases the proliferation of BECs in low androgen conditions, suggesting that the combination of 5α reductase inhibitors lowering androgen levels and PDE5-Is may be a novel, more effective treatment for BPH patients.
Keywords: CCL5; CD8+ T cell; benign epithelial cell; cyclic guanosine monophosphate/protein kinase G; nuclear factor-κB/p65.
© 2019 The Authors. The Prostate Published by Wiley Periodicals, Inc.
Conflict of interest statement
The authors declare that there are no conflict of interests.
Figures



References
-
- Gacci M, Eardley I, Giuliano F, et al. Critical analysis of the relationship between sexual dysfunctions and lower urinary tract symptoms due to benign prostatic hyperplasia. Eur Urol. 2011;60(4):809‐825. - PubMed
-
- Gacci M, Corona G, Salvi M, et al. A systematic review and meta‐analysis on the use of phosphodiesterase 5 inhibitors alone or in combination with alpha‐blockers for lower urinary tract symptoms due to benign prostatic hyperplasia. Eur Urol. 2012;61(5):994‐1003. - PubMed
-
- Oelke M, Giuliano F, Mirone V, Xu L, Cox D, Viktrup L. Monotherapy with tadalafil or tamsulosin similarly improved lower urinary tract symptoms suggestive of benign prostatic hyperplasia in an international, randomised, parallel, placebo‐controlled clinical trial. Eur Urol. 2012;61(5):917‐925. - PubMed
-
- Oelke M, Shinghal R, Sontag A, Baygani SK, Donatucci CF. Time to onset of clinically meaningful improvement with tadalafil 5 mg once daily for lower urinary tract symptoms secondary to benign prostatic hyperplasia: analysis of data pooled from 4 pivotal, double‐blind, placebo controlled studies. J Urol. 2015;193(5):1581‐1589. - PubMed
-
- Donatucci CF, Brock GB, Goldfischer ER, et al. Tadalafil administered once daily for lower urinary tract symptoms secondary to benign prostatic hyperplasia: a 1‐year, open‐label extension study. BJU Int. 2011;107(7):1110‐1116. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Research Materials
Miscellaneous

