Acute kidney injury overview: From basic findings to new prevention and therapy strategies
- PMID: 30959059
- PMCID: PMC10134404
- DOI: 10.1016/j.pharmthera.2019.04.001
Acute kidney injury overview: From basic findings to new prevention and therapy strategies
Abstract
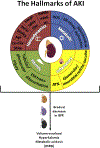
Acute kidney injury (AKI) is defined as a decrease in kidney function within hours, which encompasses both injury and impairment of renal function. AKI is not considered a pathological condition of single organ failure, but a syndrome in which the kidney plays an active role in the progression of multi-organ dysfunction. The incidence rate of AKI is increasing and becoming a common (8-16% of hospital admissions) and serious disease (four-fold increased hospital mortality) affecting public health costs worldwide. AKI also affects the young and previously healthy individuals affected by infectious diseases in Latin America. Because of the multifactorial pathophysiological mechanisms, there is no effective pharmacological therapy that prevents the evolution or reverses the injury once established; therefore, renal replacement therapy is the only current alternative available for renal patients. The awareness of an accurate and prompt recognition of AKI underlying the various clinical phenotypes is an urgent need for more effective therapeutic interventions to diminish mortality and socio-economic impacts of AKI. The use of biomarkers as an indicator of the initial stage of the disease is critical and the cornerstone to fulfill the gaps in the field. This review discusses emerging strategies from basic science toward the anticipation of features, treatment of AKI, and new treatments using pharmacological and stem cell therapies. We will also highlight bioartificial kidney studies, addressing the limitations of the development of this innovative technology.
Keywords: Acute kidney injury; Ischemia; Renal physiology; Reperfusion.
Copyright © 2019 Elsevier Inc. All rights reserved.
Conflict of interest statement
Conflict of interest statement
The authors declare that there are no conflicts of interests.
Figures
References
-
- Aksu U, Demirci C. & Ince C. (2011). The pathogenesis of acute kidney injury and the toxic triangle of oxygen, reactive oxygen species and nitric oxide. Contributions to Nephrology 174, 119–128. - PubMed
-
- Ashburn TT & Thor KB (2004). Drug repositioning: identifying and developing new uses for existing drugs. Nature Reviews Drug Discovery 3, 673–683. - PubMed
-
- Bagshaw SM, Zappitelli M. & Chawla LS (2013) Novel biomarkers of AKI: the challenges of progress ‘Amid the noise and the haste’. Nephrology Dialysis Transplantation 28, 235–238. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources

