Insights into Nano-Scale Physical and Mechanical Properties of Epoxy/Boehmite Nanocomposite Using Different AFM Modes
- PMID: 30960219
- PMCID: PMC6419076
- DOI: 10.3390/polym11020235
Insights into Nano-Scale Physical and Mechanical Properties of Epoxy/Boehmite Nanocomposite Using Different AFM Modes
Abstract
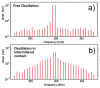
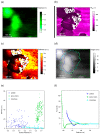
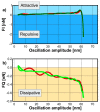
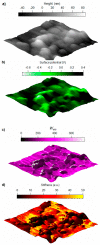
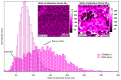
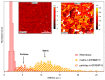
Understanding the interaction between nanoparticles and the matrix and the properties of interphase is crucial to predict the macroscopic properties of a nanocomposite system. Here, we investigate the interaction between boehmite nanoparticles (BNPs) and epoxy using different atomic force microscopy (AFM) approaches. We demonstrate benefits of using multifrequency intermodulation AFM (ImAFM) to obtain information about conservative, dissipative and van der Waals tip-surface forces and probing local properties of nanoparticles, matrix and the interphase. We utilize scanning kelvin probe microscopy (SKPM) to probe surface potential as a tool to visualize material contrast with a physical parameter, which is independent from the mechanics of the surface. Combining the information from ImAFM stiffness and SKPM surface potential results in a precise characterization of interfacial region, demonstrating that the interphase is softer than epoxy and boehmite nanoparticles. Further, we investigated the effect of boehmite nanoparticles on the bulk properties of epoxy matrix. ImAFM stiffness maps revealed the significant stiffening effect of boehmite nanoparticles on anhydride-cured epoxy matrix. The energy dissipation of epoxy matrix locally measured by ImAFM shows a considerable increase compared to that of neat epoxy. These measurements suggest a substantial alteration of epoxy structure induced by the presence of boehmite.
Keywords: atomic force microscopy; boehmite; epoxy nanocomposites; intermodulation; interphase; nanomechanical properties.
Conflict of interest statement
The authors declare no conflict of interest.
Figures






Similar articles
-
Carrier Fibers for the Safe Dosage of Nanoparticles in Nanocomposites: Nanomechanical and Thermomechanical Study on Polycarbonate/Boehmite Electrospun Fibers Embedded in Epoxy Resin.Nanomaterials (Basel). 2021 Jun 17;11(6):1591. doi: 10.3390/nano11061591. Nanomaterials (Basel). 2021. PMID: 34204405 Free PMC article.
-
Short- and Long-Range Mechanical and Chemical Interphases Caused by Interaction of Boehmite (γ-AlOOH) with Anhydride-Cured Epoxy Resins.Nanomaterials (Basel). 2019 Jun 4;9(6):853. doi: 10.3390/nano9060853. Nanomaterials (Basel). 2019. PMID: 31167417 Free PMC article.
-
Bulk chemical composition contrast from attractive forces in AFM force spectroscopy.Beilstein J Nanotechnol. 2021 Jan 18;12:58-71. doi: 10.3762/bjnano.12.5. eCollection 2021. Beilstein J Nanotechnol. 2021. PMID: 33564603 Free PMC article.
-
Identification of nanoparticles and nanosystems in biological matrices with scanning probe microscopy.Wiley Interdiscip Rev Nanomed Nanobiotechnol. 2018 Nov;10(6):e1521. doi: 10.1002/wnan.1521. Epub 2018 Apr 17. Wiley Interdiscip Rev Nanomed Nanobiotechnol. 2018. PMID: 29665287 Review.
-
Atomic force microscopy of microbial cells: application to nanomechanical properties, surface forces and molecular recognition forces.Colloids Surf B Biointerfaces. 2007 Jan 15;54(1):10-9. doi: 10.1016/j.colsurfb.2006.09.014. Epub 2006 Sep 26. Colloids Surf B Biointerfaces. 2007. PMID: 17067786 Review.
Cited by
-
Carrier Fibers for the Safe Dosage of Nanoparticles in Nanocomposites: Nanomechanical and Thermomechanical Study on Polycarbonate/Boehmite Electrospun Fibers Embedded in Epoxy Resin.Nanomaterials (Basel). 2021 Jun 17;11(6):1591. doi: 10.3390/nano11061591. Nanomaterials (Basel). 2021. PMID: 34204405 Free PMC article.
-
Short- and Long-Range Mechanical and Chemical Interphases Caused by Interaction of Boehmite (γ-AlOOH) with Anhydride-Cured Epoxy Resins.Nanomaterials (Basel). 2019 Jun 4;9(6):853. doi: 10.3390/nano9060853. Nanomaterials (Basel). 2019. PMID: 31167417 Free PMC article.
-
Probing the pH Effect on Boehmite Particles in Water Using Vacuum Ultraviolet Single-Photon Ionization Mass Spectrometry.Int J Mol Sci. 2025 Jul 27;26(15):7254. doi: 10.3390/ijms26157254. Int J Mol Sci. 2025. PMID: 40806386 Free PMC article.
-
Bulk chemical composition contrast from attractive forces in AFM force spectroscopy.Beilstein J Nanotechnol. 2021 Jan 18;12:58-71. doi: 10.3762/bjnano.12.5. eCollection 2021. Beilstein J Nanotechnol. 2021. PMID: 33564603 Free PMC article.
-
Mechanical fatigue testing in silico: Dynamic evolution of material properties of nanoscale biological particles.Acta Biomater. 2023 Aug;166:326-345. doi: 10.1016/j.actbio.2023.04.042. Epub 2023 May 2. Acta Biomater. 2023. PMID: 37142109 Free PMC article.
References
-
- May C. Epoxy Resins: Chemistry and Technology. CRC Press; Boca Raton, FL, USA: 1987.
-
- Kim B.C., Park S.W. Fracture toughness of the nano-particle reinforced epoxy composite. Compos. Struct. 2008;86:69–77. doi: 10.1016/j.compstruct.2008.03.005. - DOI
-
- Wu Z., Zhuo Q., Sun T., Wang Z. Mechanical properties of epoxy resins reinforced with synthetic boehmite (AlOOH) nanosheets. J. Appl. Polym. Sci. 2015;132 doi: 10.1002/app.41409. - DOI
-
- Arlt C. Wirkungsweisen Nanoskaliger Böhmite in Einem Polymer und Seinem Kohlenstofffaserverbund unter Druckbelastung. Otto-von-Guericke Universität Magdeburg; Magdeburg, Germany: 2011.
-
- Chen W., Wu S., Lei Y., Liao Z., Guo B., Liang X., Jia D. Interfacial structure and performance of rubber/boehmite nanocomposites modified by methacrylic acid. Polymer. 2011;52:4387–4395. doi: 10.1016/j.polymer.2011.07.028. - DOI
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Miscellaneous

